9. Malabsorption & Intolerances
 Definition
Definition
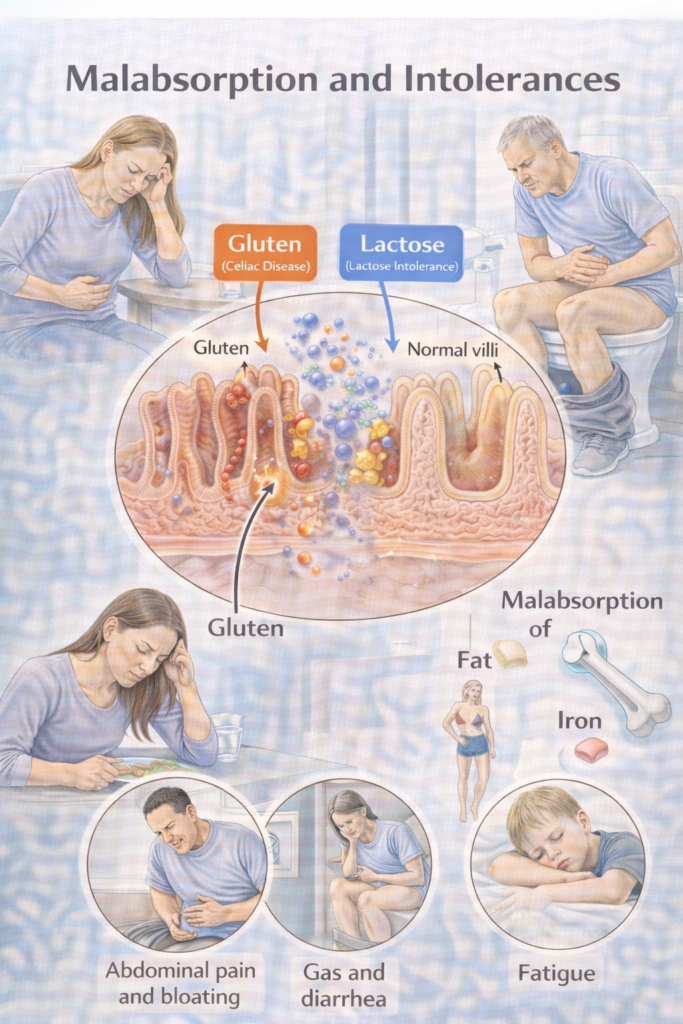
Malabsorption = impaired digestion and/or absorption of nutrients → diarrhoea (often steatorrhoea), weight loss, and micronutrient deficiencies.
Mechanistic buckets:
Intraluminal failure: inadequate digestive factors (e.g., pancreatic exocrine insufficiency [PEI], bile acid deficiency).
Mucosal failure: damaged absorptive surface (e.g., coeliac disease, Crohn’s).
Transport failure: impaired lymphatic transport (e.g., lymphangiectasia, short bowel).
 Clinical Features
Clinical Features
GI: Chronic diarrhoea (steatorrhoea = pale, greasy, difficult to flush), bloating, flatulence, abdominal discomfort.
Systemic: Weight loss, fatigue, micronutrient deficiencies (IDA, B12, folate, Vit D, Vit K).
Children: Faltering growth, delayed puberty.
Signs of deficiencies:
Iron/folate/B12 → anaemia, glossitis, neuropathy.
Vit D/Ca²⁺ → osteopenia, fractures.
Vit K → bruising, coagulopathy.
 High-Yield Hook:
High-Yield Hook:
Top 3 causes of steatorrhoea = Coeliac, PEI, BAD.
🛡️ Aetiology / Risk Factors — At-a-glance
| Domain | Examples | Clues | First actions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mucosal disease | Coeliac (autoimmune gluten-driven enteropathy), IBD | Anaemia, low Vit D, dermatitis herpetiformis (coeliac); blood/mucus (IBD) | Coeliac serology; faecal calprotectin if IBD features; endoscopy as per guideline. |
| Pancreatic causes (PEI) | Chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, post-surgery | Steatorrhoea, weight loss, fat-soluble vitamin deficiency | Faecal elastase; treat with pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT). |
| Bile-acid diarrhoea (BAD) | Ileal disease/resection, post-cholecystectomy, idiopathic | Chronic watery diarrhoea, often post-prandial | SeHCAT or serum C4/FGF19 if available; consider sequestrant trial. |
| SIBO | Motility disorders, anatomical stasis, DM, scleroderma | Bloating, diarrhoea, malabsorption ± weight loss | Breath test (variable) or empirical antibiotics in selected cases. |
| Carbohydrate intolerances | Lactose (enzyme deficiency), fructose/FODMAPs | Post-dairy bloating/diarrhoea; symptom–food link | Short exclusion → re-challenge; consider breath test if needed. |
| Infective/other | Giardia, short bowel, orlistat | Travel, greasy stools, drug history | Stool O/C/P or antigen; targeted management. |
 Red flags (When to Refer) — Table
Red flags (When to Refer) — Table
| Tier | Key triggers (examples) | Action |
|---|---|---|
 Immediate emergency Immediate emergency | Severe dehydration, shock, peritonism, GI bleed | Same-day ED/acute take |
 Urgent gastroenterology Urgent gastroenterology | 🧠 Memory Box — NG12 CRC Referral (The “4-5-6 + Mass/FIT Rule”)
| Urgent clinic; follow NG12 cancer pathways and local imaging/colonoscopy protocols |
 Routine Routine | Positive coeliac serology; chronic diarrhoea not responding to first steps; suspected BAD/PEI/SIBO without instability | Specialist pathway for confirmatory tests and targeted therapy Gut |
💡Use FIT (faecal immunochemical test) where CRC risk is suspected per NICE NG12/DG56; do not delay urgent referral if clinical concern is high.
🔬 Investigations
| Step | Investigation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Initial screen | FBC, ferritin, B12, folate, Vit D, Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, INR | Detect anaemia & deficiencies |
| Coeliac serology (tTG-IgA + total IgA) | First-line for coeliac (test on gluten) | |
| Faecal calprotectin | IBD vs functional | |
| Faecal elastase | Screen for PEI | |
| 2️⃣ Targeted | SeHCAT or serum C4/FGF19 | BAD confirmation |
| Stool O/C/P or Giardia antigen | Infective causes | |
| H₂/CH₄ breath tests | SIBO, lactose malabsorption | |
| 3️⃣ Imaging/Endoscopy | OGD + biopsies (coeliac), colonoscopy (chronic diarrhoea, red flags), MRCP/CT (pancreatic disease) | Define aetiology/extent |
 Management
Management
1) General rule: Correct deficits + treat the driver + dietitian input. (all patients)
-
-
-
Correct fluid/electrolyte & micronutrient deficits.
-
Dietitian support early.
-
Refeeding risk: replace K⁺, Mg²⁺, PO₄³⁻ if severe malnutrition.
-
-
2) Cause-specific ladders
| Cause | First-line | Escalation / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Coeliac disease | Lifelong GFD with specialist dietitian | Correct deficiencies (iron, folate, B12, Vit D, Ca²⁺). Adults need biopsy confirmation. Monitor tTG-IgA for adherence. |
| PEI (pancreatic exocrine insufficiency) | PERT (pancreatin/CREON with all meals/snacks), ADEK vitamins | Optimise dose (lipase units per g fat). Address alcohol/smoking. Nutrition support if severe. |
| Bile-acid diarrhoea (BAD) | Bile acid sequestrant (cholestyramine, colesevelam) titrated to stool control | Consider fat-soluble vitamin monitoring. Often chronic Rx. |
| SIBO | Empirical antibiotics (rifaximin, metronidazole; local protocol) | Identify/treat driver (motility disorder, strictures). May need cyclical therapy in recurrent cases. |
| Lactose intolerance / carbohydrate intolerance | Dietary exclusion to tolerance, then structured re-challenge | Lactase enzyme before dairy may help. Maintain Ca²⁺/Vit D intake. Distinguish from cow’s milk protein allergy. |
| Other (Giardia, short bowel, orlistat) | Targeted therapy (e.g., metronidazole for giardia, nutrition support for short bowel) | Stop culprit drug (e.g., orlistat). Specialist nutrition team for severe short bowel |
🔁 Follow-Up & Monitoring
| Phase | Frequency | Core checks | Escalate if… |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early (new dx / new Rx) | 6–8 weeks | Weight/BMI, stool form/frequency, symptom diary; lab correction (FBC, ferritin, B12, folate, Vit D, Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺) | Ongoing weight loss, persistent steatorrhoea/diarrhoea, new red flags |
| Established | 3–6 monthly (individualise) | Diet adherence (e.g., GFD), PERT dosing, side-effects (sequestrants), fat-soluble vitamin status | Refractory symptoms → consider combined aetiologies (e.g., coeliac + BAD, PEI + SIBO) |
🧠 Memory Boxes
Steatorrhoea triad = SPB → Small bowel (coeliac), Pancreas (PEI), Bile (BAD).
BAD test mnemonic = “See-C-at” → SeHCAT or serum C4.
Coeliac rule = Test on gluten → biopsy (adults).
PEI fix = PERT with every mouthful + ADEK vitamins.
SIBO = stasis → short antibiotic course.
Don’t miss CRC → FIT + NG12 referral.
📅 Last updated in line with
NICE NG20 — Coeliac disease: recognition, assessment and management (adults biopsy standard; children ESPGHAN criteria). NICE
NICE NG104 — Pancreatitis (malabsorption risk in chronic pancreatitis). NICE+1
UK consensus/BSG on Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency (PEI) (diagnosis, PERT). BMJ Open GastroPMC
NICE DG44 & BSG chronic diarrhoea guideline (2018/2023 page) — SeHCAT/C4 for bile-acid diarrhoea; option for empirical therapy if tests unavailable. NICEGutBritish Society of Gastroenterology
NICE DG11 — Faecal calprotectin to distinguish IBD vs non-IBD. NICE
NHS/CKS & national patient info for lactose intolerance (dietary trial ± breath testing). nhs.uk
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
