3. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Definition
Definition
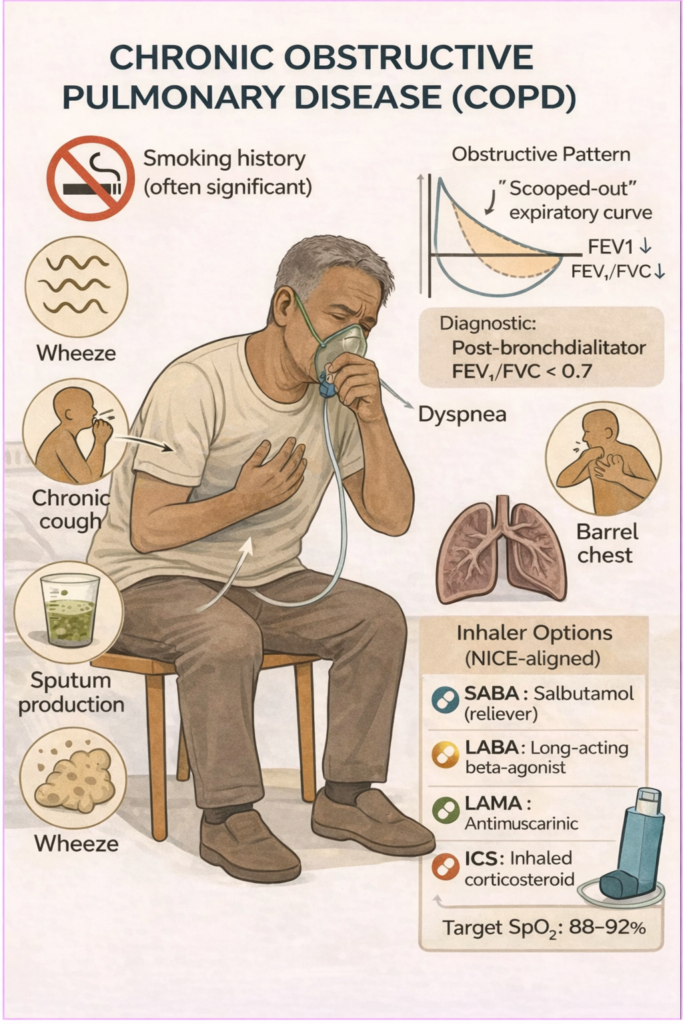
Persistent airflow obstruction that is not fully reversible due to chronic inflammation from smoking or environmental exposure.
Includes:
Chronic bronchitis: productive cough ≥3 months for ≥2 consecutive years
Emphysema: alveolar wall destruction & airspace enlargement
 Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology
Inhaled irritants (e.g. smoke) → inflammation → mucus hypersecretion + alveolar destruction
Leads to air trapping, reduced gas exchange, and increased work of breathing
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – CORE CONCEPT (PARA)
COPD = Persistent airflow obstruction that is not fully reversible
Caused by chronic exposure (usually smoking)
Includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which respiratory condition causes irreversible airflow obstruction?
👉 Answer: COPD
 Risk Factors
Risk Factors
Mnemonic: SCARE
Smoking (most important)
Cooking fuel/air pollution (biomass exposure)
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Repeated childhood infections
Environmental/occupational exposure (e.g. coal, dust)
 Clinical Features
Clinical Features
Mnemonic: COUGHED
Chronic productive cough
Overexertion causes dyspnoea
Unusual wheeze
Gradual onset of symptoms
Hyperinflated chest
Exercise limitation
Daily sputum production
📊 Diagnosis
Confirmed by spirometry
Post-bronchodilator FEV₁/FVC <0.7 (fixed obstruction)
No full reversibility (contrast with asthma)
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – DIAGNOSIS (PARA)
Spirometry is required to diagnose COPD
Post-bronchodilator FEV₁/FVC < 0.7
Obstruction is fixed (no full reversibility)
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which spirometry finding confirms a diagnosis of COPD?
👉 Answer: Post-bronchodilator FEV₁/FVC < 0.7
Other investigations:
CXR: rule out malignancy, assess hyperinflation
Alpha-1 antitrypsin: if <40 yrs or FHx
FBC: polycythaemia (from chronic hypoxia)
Sputum culture: if recurrent exacerbations
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – ASTHMA vs COPD (PARA)
Asthma → reversible airflow obstruction
COPD → irreversible airflow obstruction
Smoking history strongly favours COPD
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which feature best differentiates COPD from asthma?
👉 Answer: Lack of reversibility on spirometry
🩻 CXR Findings
Mnemonic: HEAVES
Hyperinflated lungs
Elongated heart shadow
Attenuated vessels (vascular markings ↓)
Vertical heart
Emphysematous bullae
Small peripheral markings (loss of definition)
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – IMAGING (PARA)
CXR may show hyperinflation or bullae
Imaging does not confirm COPD
Diagnosis must be made with spirometry
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Can a chest X-ray confirm a diagnosis of COPD?
👉 Answer: No
Severity
Based on FEV₁ % predicted:
| Severity | FEV₁ % | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mild | ≥80% | Often underdiagnosed |
| Moderate | 50–79% | Symptoms with exertion |
| Severe | 30–49% | Symptoms at rest |
| Very Severe | <30% | Risk of respiratory failure |
Also use MRC Dyspnoea Scale (Grade 1–5) to assess breathlessness:
| Grade | Degree of Breathlessness |
| 1 | Not troubled by breathlessness except on strenuous exercise. |
| 2 | Short of breath when hurrying or walking up a slight hill. |
| 3 | Walks slower than contemporaries on level ground or has to stop for breath when walking at own pace. |
| 4 | Stops for breath after walking about 100 metres or after a few minutes on level ground. |
| 5 | Too breathless to leave the house, or breathless when dressing or undressing. |
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – SEVERITY & SYMPTOMS (PARA)
FEV₁ % predicted assesses airflow limitation
MRC dyspnoea scale assesses symptom burden
Treatment escalation is guided by symptoms and exacerbations
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which tool is used to assess breathlessness severity in COPD?
👉 Answer: MRC dyspnoea scale
Management
Mnemonic: STOP
Smoking cessation – most important
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – MOST IMPORTANT INTERVENTION (PARA)
Smoking cessation is the single most effective intervention
Slows disease progression
Improves survival
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What is the most important intervention to slow COPD progression?
👉 Answer: Smoking cessation
Terbutaline/Salbutamol (SABA) or Ipratropium (SAMA) for quick relief.
Oxygen (LTOT) if PaO₂ ≤7.3 kPa (or ≤8.0 kPa with peripheral oedema, polycythaemia, or pulmonary hypertension.)
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – LONG-TERM OXYGEN THERAPY (LTOT) (PARA)
Indicated in stable COPD if:
PaO₂ ≤7.3 kPa (or ≤8.0 kPa with complications)
Improves survival in chronic hypoxia
- To qualify for LTOT, the patient must have stopped smoking.
- Providing oxygen to a current smoker is a major fire risk and a common ‘Safety Trap’ in the exam.
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What arterial oxygen threshold indicates long-term oxygen therapy in COPD?
Pulmonary rehab for MRC ≥3
Mnemonic: BREAD
Bronchodilators (The “Two-Path” Step):
| Path A: No Asthmatic Features | Path B: With Asthmatic Features |
| First Line: LABA + LAMA | First Line: LABA + ICS |
| (e.g. Aclidinium/Formoterol) | (e.g. Salmeterol/Fluticasone) |
| ↓ | ↓ |
| If still symptomatic: | If still symptomatic: |
| LABA + LAMA + ICS (Triple Therapy) | LABA + LAMA + ICS (Triple Therapy) |
Rescue Pack (Steroids + Antibiotics for home use).
Exacerbation management (5 days Prednisolone/5 days Antibiotics).
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin screening (if young/non-smoker).
Diet/BMI monitoring (NICE emphasizes nutrition in chronic lung disease).
Exacerbation Management
Mnemonic: COPD-X
C — Controlled Oxygen
Target SpO₂ 88–92%
Use Venturi mask (or nasal cannula if stable)
Repeat ABGs if severe, drowsy, or hypercapnia suspected
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – OXYGEN (PARA)
📌 PARA commonly asks:
A patient with known COPD presents with an acute exacerbation. What oxygen saturation target should be used?
👉 Answer: 88–92%
O — Optimise Bronchodilators
Duonebs: salbutamol or ipratropium (neb or inhaler with spacer)
Increase frequency during acute phase
 EXAM ANCHOR – BRONCHODILATORS (PARA)
EXAM ANCHOR – BRONCHODILATORS (PARA)

What is the first-line bronchodilator regimen in an acute COPD exacerbation?

D — Decide Antibiotics (If Indicated)
Give antibiotics only if infective features present:
↑ sputum purulence
± ↑ sputum volume
± ↑ dyspnoea
Send sputum culture if severe or recurrent exacerbations
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – ANTIBIOTICS (PARA)
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Question:
When are antibiotics indicated in an acute COPD exacerbation?
👉 Answer: Antibiotics if increased sputum purulence PLUS (increased dyspnoea OR increased sputum volume).
X — eXclude Complications & Escalate Care
CXR to exclude pneumonia or pneumothorax
Admit if confusion, cyanosis, worsening hypoxia, exhaustion, or haemodynamic instability
Consider NIV if persistent hypercapnic respiratory acidosis despite optimal medical therapy
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – NIV (PARA)
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Question:
When should non-invasive ventilation (NIV) be considered in an acute COPD exacerbation?
👉 Answer: Persistent hypercapnic respiratory acidosis despite optimal medical therapy
Monitoring & Review
Annual review (inhaler technique, adherence, symptoms)
Monitor MRC dyspnoea scale, exacerbation frequency, BMI
Consider home rescue pack (antibiotic + steroid) for frequent exacerbators
 Complications
Complications
Mnemonic: CHAP
Cor pulmonale (right heart failure)
Hypercapnic respiratory failure
Acute exacerbations
Pneumothorax (esp. in bullous disease)
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – COMPLICATIONS (PARA)
Chronic hypoxia → polycythaemia
Pulmonary vascular disease → cor pulmonale
Bullous disease → pneumothorax
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which complication of COPD results from chronic hypoxia?
👉 Answer: Cor pulmonale
Differential Diagnoses
Mnemonic: ABC LUNG
Asthma
Bronchiectasis
CHF
Lung cancer
Upper airway obstruction
Neuromuscular disease
GORD-associated cough
 Key PARA Exam Traps – COPD
Key PARA Exam Traps – COPD




• Frequent exacerbations (≥2/year or ≥1 hospital admission) despite bronchodilators, or
• Steroid responsiveness (e.g. asthma history or blood eosinophils ≥300 cells/µL)





Last updated in line with NICE NG115 (March 2023)
Reviewed for PassMap: Febuary 2026
This content is NICE-compliant and exam-optimised for the Physician Associate Regulation Assessment (PARA).
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
