8. Coeliac Disease
 Definition
Definition
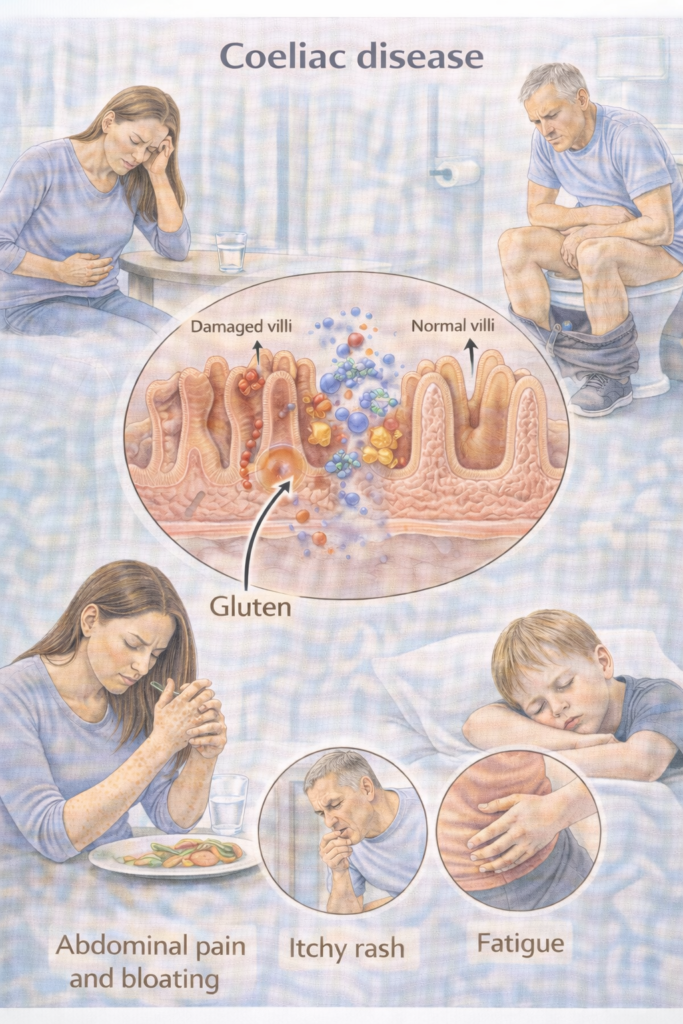
Coeliac disease is an autoimmune, gluten-driven enteropathy causing small-bowel mucosal damage and malabsorption in genetically susceptible people (HLA-DQ2/DQ8 haplotypes). Lifelong GFD (gluten-free diet) is the treatment.
 Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology
| Step | Pathophysiology | Exam clue |
|---|---|---|
 Gluten peptides Gluten peptides | Gliadin fragments reach lamina propria | Trigger antigen |
 tTG deamidation tTG deamidation | Increases HLA-DQ2/8 binding | Anti-tTG antibodies |
 T-cell activation T-cell activation | IFN-γ release, inflammation | Villous atrophy |
 B-cell activation B-cell activation | Anti-tTG, EMA, DGP antibodies | Used for serology |
 Mucosal damage Mucosal damage | Villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia | Malabsorption (iron, folate, Ca, Vit D) |
 Mnemonic — “4A’s in Coeliac”
Mnemonic — “4A’s in Coeliac”
Autoimmunity (anti-tTG, EMA, DGP antibodies)
Atrophy (villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia)
Absorption loss (malabsorption: diarrhoea, steatorrhoea, anaemia)
Associated risk (Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL), adenocarcinoma, osteoporosis, other autoimmune conditions like T1DM, thyroid disease)
🛡️ Aetiology / Risk Factors — At-a-glance
| Domain | Key points |
|---|---|
| Genetic | Strong association with HLA-DQ2/DQ8 (common, not diagnostic alone). |
| Autoimmune links | Type 1 diabetes, autoimmune thyroid disease, autoimmune liver disease. |
| Family history | First-degree relatives (offer testing). |
| Associated conditions | Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH), Down/Turner syndrome, IgA deficiency. |
 Clinical Features
Clinical Features
-
GI: chronic/intermittent diarrhoea, bloating, abdominal pain, steatorrhoea, constipation (sometimes).
-
Systemic: iron/folate/B12 deficiency, weight loss, fatigue, osteopenia/osteoporosis.
-
Dermatology: DH (intensely itchy vesicular rash—elbows/knees/buttocks).
-
Children: faltering growth, delayed puberty, irritability.
 When to Test / Refer (NICE NG20)
When to Test / Refer (NICE NG20)
Who to test (serology): people with persistent GI symptoms or risk groups: IDA (iron-deficiency anaemia), weight loss, severe mouth ulcers, fatigue, type 1 diabetes at diagnosis, autoimmune thyroid disease, adults meeting IBS criteria, first-degree relatives, children with faltering growth. Test while eating gluten.
Referral pathway (adults & YP):
Positive serology → refer to GI for endoscopic duodenal biopsy to confirm/exclude coeliac disease. (NICE does not endorse adult “no-biopsy” diagnosis.)
Suspected DH → dermatology for skin biopsy with granular IgA + coeliac work-up.
🔬 Investigations (support a positive diagnosis)
| Test | Why / When | How / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Serology: IgA tTG (tissue transglutaminase IgA) + total IgA | First-line screen | If IgA deficient → use IgG-based assay (IgG-DGP/IgG-tTG). Must be on gluten. |
| IgA EMA (endomysial antibody) | Confirmatory when tTG weakly positive | Improves specificity before referral. |
| OGD + duodenal biopsies | Diagnostic standard (adults) | Multiple biopsies, including bulb, while on gluten. |
| HLA-DQ2/DQ8 typing | Rule-out in equivocal cases or after GFD | Negative DQ2/DQ8 → coeliac very unlikely; positive ≠ diagnostic. |
| Children (ESPGHAN 2020) | Selected no-biopsy pathway | If tTG-IgA ≥10× ULN and EMA-IgA positive, compatible picture → no biopsy acceptable; HLA not required. Specialist led. |
| Baseline deficiencies | Malabsorption profile | FBC, ferritin, B12, folate, vitamin D, calcium, LFTs. (Bone risk). |
Gluten challenge (already on GFD): protocols vary; typical adult approach is ≥3–10 g gluten/day for 2–8 weeks prior to repeat serology/biopsy (specialist advice; balance symptoms vs yield).
 Management — Stepwise Ladder
Management — Stepwise Ladder

Do not start a GFD. Take coeliac serology while eating gluten. Safety-net re: worsening symptoms/weight loss.

Adults: OGD (oesophagogastroduodenoscopy) with duodenal biopsies (per NG20). Children: follow ESPGHAN no-biopsy criteria where eligible (specialist).

Lifelong GFD with specialist dietitian input (label reading, cross-contamination, eating out, school/work).
Treat deficiencies (iron/B12/folate/vitamin D/calcium). Dental and fracture risk counselling.

Consider pneumococcal vaccination if hyposplenism suspected; ensure routine immunisations up to date.
Lifestyle: weight/fitness; manage osteoporosis risk. (Bone health below.)

Check hidden gluten, diet adherence (dietetic review), IBD, microscopic colitis, SIBO, pancreatic insufficiency, lactose intolerance; coeliac serology trend. Specialist referral for refractory coeliac disease.

Gluten-free staple foods on NHS prescription are restricted by locality (often bread/flour only). Advise on supermarket options and Coeliac UK resources.
🔁 Follow-Up & Monitoring
| Phase | When | What to check | Escalate if… |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early | 3–6 months after diagnosis | Symptoms, diet adherence, weight/BMI; tTG-IgA trend; FBC, ferritin, B12, folate, vitamin D, calcium, LFTs | No serology improvement, persistent symptoms, weight loss |
| Established | 12 months, then annually | As above; address vaccines, pregnancy planning, mental health/quality of life | Ongoing deficiency, abnormal LFTs, osteoporotic fracture |
| Bone health | Consider DEXA (bone density) if high risk (long delay to diagnosis, fractures, post-menopause, men >55 with risk) | Calcium/vitamin D; weight-bearing exercise | Low BMD or fractures → osteoporosis pathway |
Quality Standard (QS134): aim for biopsy within 6 weeks of referral when serology is positive.
🧭 When to Refer — Table
| Tier | Key triggers | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 🚑 Immediate | Severe dehydration, haemodynamic instability, suspected severe malabsorption with syncope | Same-day ED/acute take |
| ⚡ Urgent GI | Positive serology, unexplained IDA/weight loss, persistent diarrhoea, dermatitis herpetiformis | GI/dermatology clinic; arrange OGD + biopsies (adults) |
| 📮 Routine | Confirmed coeliac needing dietetic optimisation, non-responsive symptoms without red flags | IBD/coeliac service or community dietetics; consider causes of NRCD |
🧠 Memory Boxes
“Test on gluten”: take tTG-IgA + total IgA before any diet change; if IgA-deficient → IgG-DGP/IgG-tTG.
Adults: biopsy to diagnose (NICE NG20). Children: ESPGHAN no-biopsy allowed if tTG-IgA ≥10× ULN + EMA-IgA positive.
Deficiencies: think iron/folate/B12/Vit D/calcium; consider DEXA if risks.
Non-response: gluten exposure first, then look for IBD/microscopic colitis/SIBO.
 Last updated in line with
Last updated in line with
NICE NG20 (Coeliac disease: recognition, assessment and management) — Published 2 Sep 2015, current online content; 2019 surveillance retained biopsy-based diagnosis in adults. NICE+1
NICE QS134 (Coeliac disease – Quality Standard) — Biopsy within 6 weeks of referral. NICE
ESPGHAN 2020 (Paediatric no-biopsy pathway). ESPGHAN
BSG (British Society of Gastroenterology) adult guideline — current page notes under review for 2025; use alongside NICE. British Society of Gastroenterology
NHS England (Gluten-free foods prescribing policy) — local restriction of items (commonly bread/flour). NHS England
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
