5. Hypotension
 Definition
Definition
Hypotension refers to abnormally low blood pressure, typically defined as:
SBP <90 mmHg or
MAP <65 mmHg
Can be acute (e.g. in shock) or chronic/asymptomatic.
📊 Types of Hypotension
Orthostatic (Postural): >20 mmHg systolic or >10 mmHg diastolic drop on standing within 3 minutes.
Shock-related: due to circulatory collapse (e.g. sepsis, cardiogenic shock).
Neurogenic: spinal injury or autonomic dysfunction.
Drug-induced: antihypertensives, diuretics, nitrates, anaesthetics.
 Aetiology
Aetiology
 Mnemonic: SHOCKED
Mnemonic: SHOCKED
Sepsis (vasodilation)
Haemorrhage/hypovolaemia
Obstruction (e.g. PE, tamponade)
Cardiogenic (e.g. MI, arrhythmias)
K (Potassium – electrolyte imbalance)
Endocrine (Addison’s, hypothyroid)
Drugs (e.g. antihypertensives, alcohol)
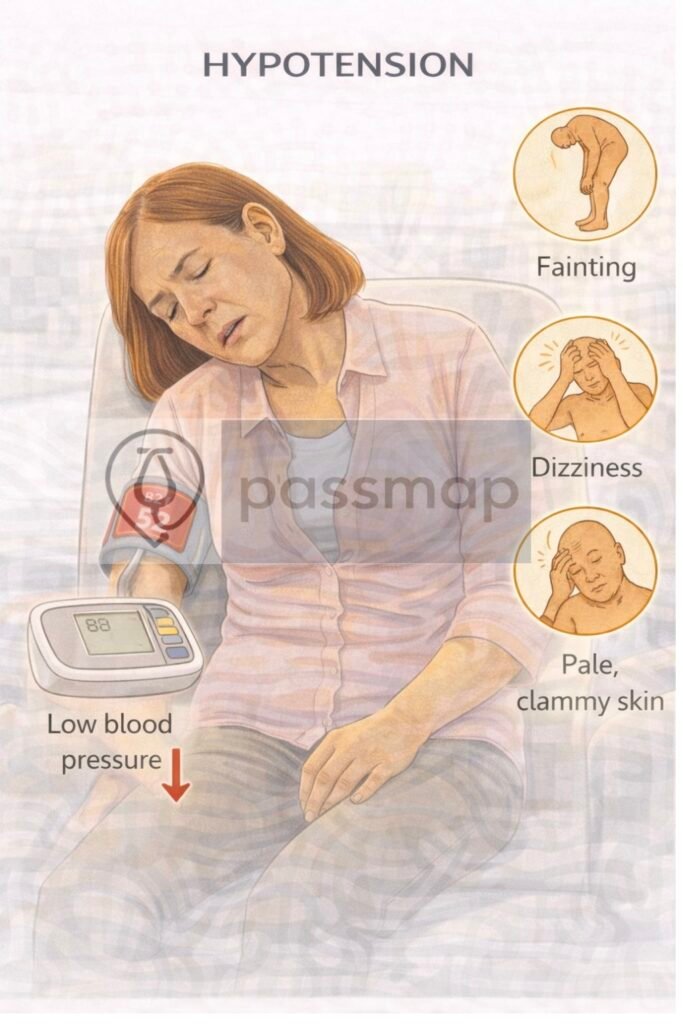
🩺Clinical Features
Dizziness or light-headedness
Syncope or near-syncope
Blurred vision
Fatigue
Nausea
Cold, clammy extremities (in shock)
🔬Investigation
Observations: BP lying & standing, HR, RR, SpO2
ECG: arrhythmias or MI
FBC, U&Es: anaemia, dehydration
Lactate: shock indicator
Cortisol/ACTH: adrenal insufficiency
TFTs, glucose: endocrine causes
CXR, echo, CT: structural or septic causes (if unwell)
Management
🧠 Mnemonic: PRESSURE
Position (lying flat, legs elevated)
Review medications
Exclude life-threatening causes (shock)
Saline IV fluids (0.9% NaCl)
Sepsis protocol if suspected
Use vasopressors in ICU if needed
Reassess after intervention
Educate on lifestyle changes (hydration, slow standing)
 Red Flags
Red Flags
SBP <90 mmHg with symptoms
Suspected sepsis, MI, PE, or adrenal crisis
Falls or unexplained syncope
New onset postural hypotension in elderly
🔎 Key PARA Exam Traps
💡 MAP Calculation: You might be asked to calculate the Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP).
💡Beta-Blocker Overdose: If a patient is hypotensive and bradycardic, think Beta-blocker or Calcium Channel Blocker overdose. The antidote often used in exams is Glucagon.
💡Pulmonary Embolism (PE): If the patient is hypotensive with a suspected PE, they are classified as a “Massive PE.” The “next step” changes from anticoagulation to Thrombolysis
🔺 Last updated in line with BMJ Best Practice (2025/2026) – Assessment of Hypotension • Last updated: October 2025
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026

Educational platform. Not medical advice.
