5.2. Tuberculosis (TB)
 Definition
Definition
Tuberculosis (TB) is a chronic infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, commonly affecting the lungs (pulmonary TB) but may involve any organ (extrapulmonary TB).
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – CORE CONCEPT
Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Transmitted via airborne droplets
Can be pulmonary or extrapulmonary
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What organism causes tuberculosis?
🔬 Pathophysiology
Inhaled droplets → alveolar macrophage phagocytosis
Formation of granulomas (caseating necrosis)
Can be:
Latent TB – asymptomatic, non-infectious
Active TB – symptomatic, infectious
Reactivation common in immunosuppressed
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – LATENT vs ACTIVE TB
Latent TB: asymptomatic, non-infectious
Active TB: symptomatic and infectious
Reactivation risk ↑ in immunosuppression
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What distinguishes latent TB from active TB?
📋 Risk Factors
🧠 Mnemonic: CLOSE CONTACT
Contact with known TB case
Low immunity (HIV, diabetes, cancer, steroids)
Overcrowded living (hostels, prisons)
Socioeconomic deprivation
Endemic area travel/residence (Africa, SE Asia)
Chronic renal failure
Organ transplant
Nutritional deficiency
Teenagers or elderly
Alcohol misuse
Chemotherapy
Tobacco smoking
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – RISK FACTORS
Close contact with TB case
Immunosuppression (HIV, steroids)
Endemic exposure
Overcrowding / homelessness
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which factor increases the risk of tuberculosis reactivation?
 Clinical Features
Clinical Features
🧠 Mnemonic: CLAPS
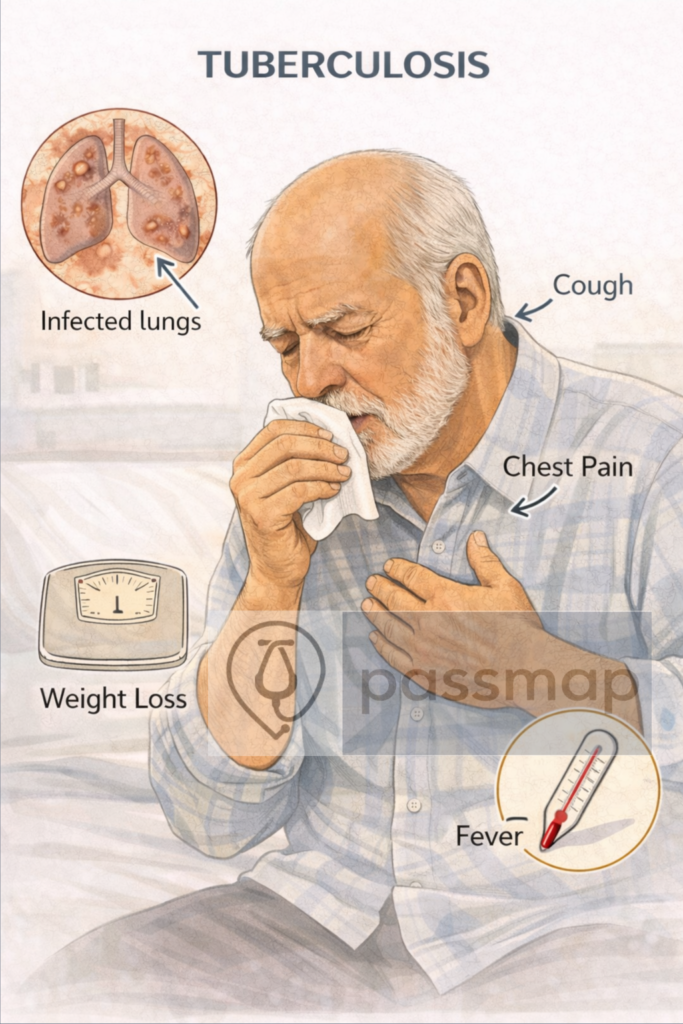
Cough >3 weeks (± haemoptysis)
Low-grade fever (especially evening)
Anorexia and weight loss
Profuse night sweats
SOB and pleuritic chest pain
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Cough >3 weeks
Weight loss
Night sweats
± haemoptysis
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which symptom combination is most suggestive of pulmonary TB?
🩺 Physical Examination Findings
Cachexia, pallor, lymphadenopathy
Finger clubbing
Crackles/bronchial breathing
Spinal tenderness (if Pott’s disease)
Signs of effusion or consolidation
🔍 Investigations
🧠 Mnemonic: SPUTUM CXR TEST
Sputum: 3 early-morning samples → Ziehl-Neelsen stain, culture (8 weeks), PCR
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – DIAGNOSIS
Sputum microscopy, culture, and PCR
3 early-morning sputum samples
Culture confirms diagnosis
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What is the definitive diagnostic test for pulmonary TB?
CXR: upper lobe infiltrates ± cavitation, hilar lymphadenopathy
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – IMAGING
Pulmonary TB classically affects upper lobes
Cavitation is a typical feature
Normal early CXR does not exclude TB
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which lung region is classically affected in pulmonary TB?
Mantoux test (tuberculin skin test)
IGRA (Interferon Gamma Release Assay) – e.g. T-Spot TB
HIV test
FBC, LFTs – baseline for treatment
CT/MRI – for extrapulmonary TB
Pleural aspirate/biopsy – if pleural TB suspected
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – IMMUNOLOGICAL TESTING
Mantoux / IGRA detect TB exposure
Cannot distinguish latent from active TB
Used with clinical and imaging findings
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What does a positive IGRA indicate?
Extrapulmonary TB (EPTB)
🧠 Mnemonic: SPINE
Spinal TB (Pott’s disease)
Pericardial TB
Intestinal TB
Neuro TB (meningitis)
Effusions (pleural, peritoneal, joint)
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – EXTRAPULMONARY TB
TB can affect lymph nodes, spine, CNS, kidneys
Pott’s disease = spinal TB
CNS TB requires prolonged treatment
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What is Pott’s disease?
🧾 Management
🧠 Mnemonic: RIPE
Rifampicin
Isoniazid
Pyrazinamide
Ethambutol
Duration:2 months RIPE → 4 months RI (total 6 months)
12 months for CNS/spinal TB
💊 Co-prescribe pyridoxine (vitamin B6) with isoniazid to prevent neuropathy
🛡️ Public Health:
Notifiable disease
Close contact tracing
DOT (Directly Observed Therapy) if adherence is a concern
Consider isolation if smear-positive
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – MANAGEMENT REGIMEN
RIPE regimen for drug-sensitive TB
Standard pulmonary TB = 6 months
CNS/spinal TB = 12 months
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What is the standard first-line drug regimen for tuberculosis?
⚠️ Side Effects of Treatment
🧠 Mnemonic: RIPE SIDE
Rifampicin – red/orange secretions, hepatotoxicity
Isoniazid – neuropathy, hepatitis
Pyrazinamide – gout, hepatotoxic
Ethambutol – optic neuritis (visual testing needed)
🧐 Differentials
🧠 Mnemonic: CHILD COUGH
Cancer
Histoplasmosis
Interstitial lung disease
Lung abscess
Drug reaction (ACE-i)
COPD
Oesophageal reflux
Urinary TB (if systemic)
Granulomatosis (e.g. sarcoidosis)
HIV-related opportunistic infection
📌 PARA Revision Tips
Always isolate suspected smear-positive TB
Weight loss + night sweats + cough >3 weeks = TB unless proven otherwise
Know the RIPE regimen, duration, and public health actions
CXR + sputum + IGRA/Mantoux = triple approach
Risk of reactivation high in HIV/steroid use
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – PUBLIC HEALTH
TB is a notifiable disease
Contact tracing required
Smear-positive TB → respiratory isolation
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What immediate public health action is required in smear-positive TB?
🔎 Key PARA Exam Traps
💡 TB presents insidiously → weight loss, night sweats, chronic cough, haemoptysis
💡 Pulmonary TB classically affects the upper lobes (apical disease)
💡 Normal early CXR does not exclude TB: High suspicion → further testing
💡 Sputum AFB samples (×3) are required: Early morning samples increase yield
💡 Culture confirms diagnosis but takes weeks: Treatment may start before confirmation if suspicion high
💡 Latent TB = asymptomatic, non-infectious: Positive IGRA / Mantoux with normal CXR
💡 Active TB is infectious: Requires respiratory isolation (exam favourite)
💡 Extrapulmonary TB is common: Think lymph nodes, spine (Pott disease), kidneys, CNS
💡 Always assess TB risk factors: Birth/travel in endemic areas, homelessness, immunosuppression, HIV
💡 Steroids are indicated in specific TB forms: e.g. TB meningitis, pericarditis (trap)
🔎 Last updated in line with NICE NG33 – Tuberculosis
Published: January 2016 • Last updated: September 2019
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
🔒 PASSMAP ensures all content is NICE-aligned and reviewed for Physician Associate Registration Assessment (PARA) success.
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
