3.4. Hypertension
 Definition
Definition
Hypertension is defined as persistently elevated arterial blood pressure. Diagnosis is confirmed by out-of-office measurement.
Stage 1: Clinic BP ≥140/90 mmHg AND ABPM/HBPM ≥135/85 mmHg
Stage 2: Clinic BP ≥160/100 mmHg AND ABPM/HBPM ≥150/95 mmHg
Severe: Clinic systolic ≥180 mmHg OR diastolic ≥120 mmHg
Treat Stage 1 if the patient is <80 years old AND has end-organ damage, CVD, Renal disease, Diabetes, or a QRISK3 ≥10%. If none of these are present, offer lifestyle advice and monitor.
🔍 PASSMAP Insight
The GMC combines “arterial thrombosis” and “hypertension” in the core condition list to emphasise how long-term vascular damage from high blood pressure leads to life-threatening thrombotic events such as MI, stroke, and limb ischaemia.
 Risk Factors
Risk Factors
Age >55 (men), >65 (women)
Black African or Caribbean ethnicity
Obesity
Smoking
Diabetes
Excess alcohol intake
Family history of hypertension or cardiovascular disease
QRISK3: 10-Year Cardiovascular Risk Assessment
QRISK3 is a validated clinical algorithm used in the UK to calculate a patient’s percentage risk of having a major cardiovascular event (heart attack or stroke) over the next 10 years.
1. The 10% Threshold
Result >10% or equal Classed as “High Risk.”
Action: Offer Atorvastatin 20mg (primary prevention) and consider medication for Stage 1 Hypertension.
2. When to Calculate It
Stage 1 Hypertension: Use it to decide if a patient needs medication immediately.
Primary Prevention: Routine health checks for adults aged 40–74.
3. When NOT to Use It (Already High Risk)
You do not need a QRISK score for these patients; they are eligible for statins automatically:
Existing CVD: Already had a Stroke, TIA, or MI.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Specifically if eGFR $< 60$.
Type 1 Diabetes: (If >40 years old or had the condition for > 10 years).
Familial Hypercholesterolaemia: Genetic high cholesterol.
4. Key Inputs
It factors in more than just BP and cholesterol. It includes:
Demographics: Age, ethnicity, and postcode (deprivation).
Conditions: AF, RA, SLE, Migraines, and Severe Mental Illness.
Meds: Chronic steroid use or atypical antipsychotics.
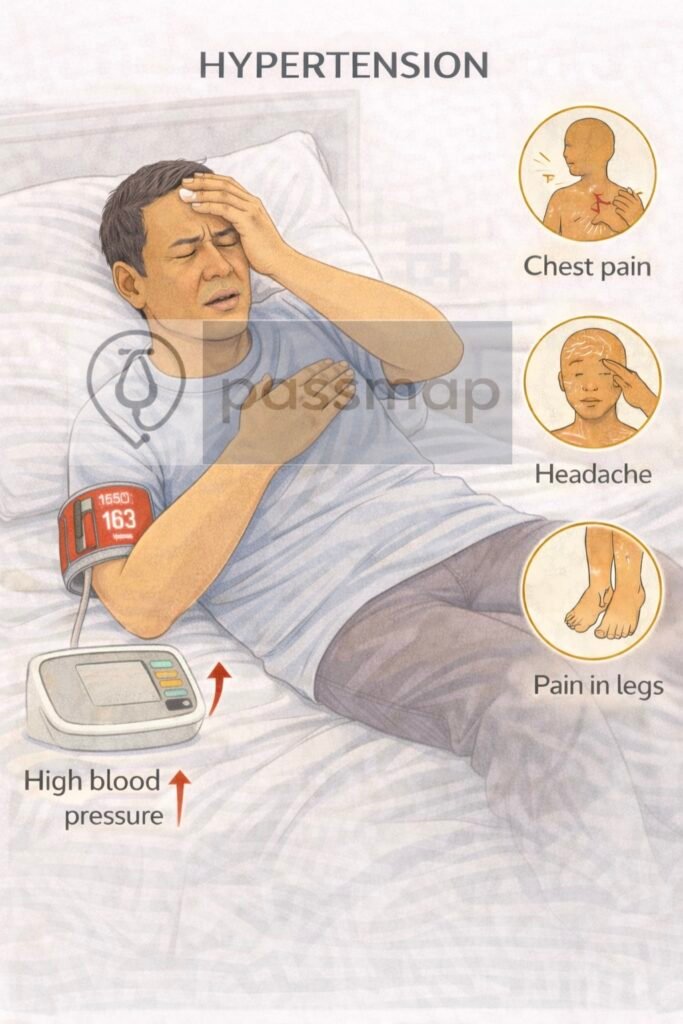
 Clinical Features
Clinical Features
Most cases are asymptomatic.
 Symptoms suggest complications:
Symptoms suggest complications:
Headache (esp. in severe/malignant HTN)
Visual disturbances (retinopathy)
Chest pain / dyspnoea (LVH, HF)
Neurological symptoms (stroke, TIA)
 Investigations
Investigations

HbA1c (diabetes)
Yield: ABPM/HBPM for diagnosis
Proteinuria/ACR & U&Es (renal function)
ECG (LVH, arrhythmia)
Retinopathy (fundoscopy)
Total cholesterol/lipids
EGFR & creatinine
Natrium (Sodium), potassium
Secondary causes (young, resistant HTN)
Invest for end-organ damage
Observe lifestyle factors
Non-invasive CV risk score (QRISK3)
💊 Management
🧠 Mnemonic: A-C-D Rule (age, ethnicity, and diabetes-based)
➡️ Step 1:
Age <55 and no diabetes: ACEi or ARB
Age ≥55 or Black African/Caribbean ethnicity (any age, no diabetes): CCB
Diabetes (any age or ethnicity): ACEi or ARB
➡️ Step 2: Combine A + C (ACEi/ARB + CCB)
➡️ Step 3: Add D (thiazide-like diuretic e.g. indapamide)
➡️ Step 4: Consider low-dose spironolactone
- if K+ ≤4.5 or higher-dose thiazide-like diuretic
- if K+ >4.5. Seek specialist advice for resistant HTN.
💡 All patients:
Lifestyle advice (weight loss, salt restriction, DASH diet, physical activity)
Statin if 10-year CV risk ≥10% (QRISK3)
🎯 2026 Exam Cheat Sheet: Hypertension “Must-Knows”
When tackling a hypertension case, follow this flow:
Diagnosis: Clinic ≥140/90? $\rightarrow$ Offer ABPM/HBPM.
Screening: Check Urine ACR (Albumin:Creatinine Ratio), ECG, and Fundoscopy for end-organ damage.
Treatment Choice:
Diabetic? ACEi (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme inhibitor) regardless of age/ethnicity.
Black ethnicity or Age ≥55? CCB (Calcium Channel Blocker).
Targets:
<80 years: <140/90 (Clinic) or <135/85 (Home).
80 years: <150/90 (Clinic) or <145/85 (Home).
 Complications
Complications
MI, stroke, TIA
Heart failure
CKD
Retinopathy
Aortic dissection
🩺 Monitoring
Monitor BP every 4–6 weeks until controlled, then 6–12 monthly
Monitor U&Es if on ACEi, diuretic, or spironolactone
Annual QRISK3 update
To align with the latest 2026 clinical standards and the Physician Associate Registration Assessment (PARA) blueprint, this section has been updated to reflect the most recent consensus on treatment targets and the management of Stage 1 hypertension.
📅 Verification & Compliance Update
Last updated in line with:
NICE NG136 (2025/26 Consolidated Update): Specifically addressing the use of QRISK3 thresholds and the aggressive management of younger patients (<40 years).
NICE TA (Technology Appraisals) 2025: Regarding the role of automated home blood pressure monitoring systems in primary care.
BHS (British Hypertension Society) 2026 Guidelines: On the integration of lifestyle “prescriptions” alongside pharmacological steps.
PARA/MLA-aligned: Fully reviewed February 2026 for current UK national assessment standards.
🔒 PASSMAP Assurance: This content is peer-reviewed, NICE-compliant, and optimized for the GMC Medical Licensing Assessment (MLA) and PA National Exam (PARA).
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
