 Definition
Definition
Lung Malignancy is a malignant tumour originating in the lung tissue. It is the leading cause of cancer-related death in the UK.
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – CORE CONCEPT
Lung malignancy is a malignant tumour of lung tissue
Smoking is the strongest risk factor
Leading cause of cancer-related death in the UK
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What is the strongest risk factor for lung cancer?
🔬 Pathophysiology
Uncontrolled growth of abnormal lung epithelial cells, often linked to carcinogen exposure (e.g. smoking, asbestos).
Two Main Types:
NSCLC (Non-small cell lung cancer – ~85%)
– Adenocarcinoma (peripheral), squamous cell carcinoma (central), large cell carcinomaSCLC (Small cell – ~15%)
– Aggressive, early metastasis, strong paraneoplastic links
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – CANCER TYPES
NSCLC ≈ 85% of cases
SCLC ≈ 15%, aggressive with early metastasis
Management differs significantly
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which type of lung cancer accounts for the majority of cases?
📋 Risk Factors
🧠 Mnemonic: CARS SMOKE
Chronic lung disease (COPD, ILD)
Asbestos exposure
Radon gas
Secondhand smoke
Smoking (most important)
Male sex
Occupational dusts (arsenic, chromium, silica)
Kin history (family)
Environmental pollution
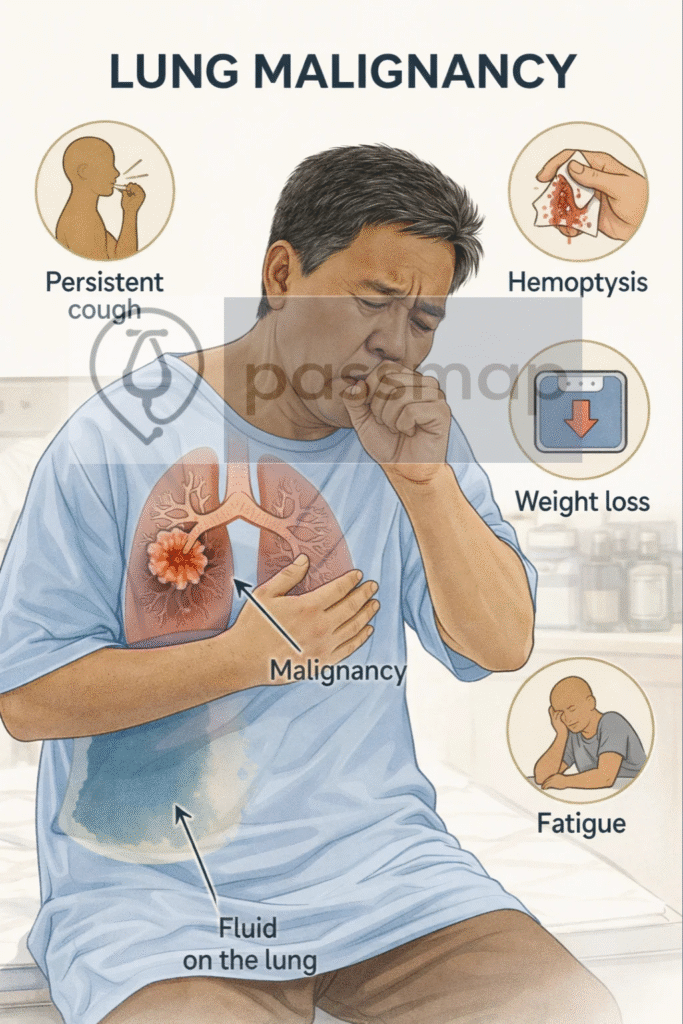
 Clinical Features
Clinical Features
🧠 Mnemonic: SPHERE
Symptoms: cough (persistent/new/change), dyspnoea
Pain: chest pain
Haemoptysis
Effusion (pleural)
Recurring infections (e.g. pneumonia)
Energy low (weight loss, fatigue)
🧠 Late signs: hoarseness (recurrent laryngeal nerve), SVC obstruction, clubbing, Horner’s syndrome, bone pain, seizures (mets)
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Persistent cough
Haemoptysis
Weight loss
Recurrent chest infections
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which symptom combination should raise suspicion of lung cancer?
Paraneoplastic Syndromes (Especially in SCLC)
🧠 Mnemonic: LEAD
Lambert-Eaton (proximal weakness, improves with use)
Ectopic ACTH (Cushing’s)
ADH → SIADH
Dermatological (acanthosis, hypercalcaemia in squamous cell)
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – PARANEOPLASTIC SYNDROMES
SCLC → SIADH, ectopic ACTH, Lambert–Eaton
Squamous cell carcinoma → hypercalcaemia
Paraneoplastic features may precede diagnosis
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which lung cancer is most associated with SIADH?
🔎 Investigations
🧠 Mnemonic: CXR CT PET
CXR: 1st-line for persistent cough ≥3 weeks
CT thorax with contrast: confirms lesion
PET-CT: staging
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – STAGING
PET-CT used for staging
MRI brain if neurological symptoms
Staging determines management
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What investigation is required to confirm a diagnosis of lung cancer?
Bronchoscopy + biopsy
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – IMAGING & DIAGNOSIS
CXR = first-line investigation
CT chest confirms lesion
Tissue biopsy (Histology) required for diagnosis
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What investigation is required to confirm a diagnosis of lung cancer?
Sputum cytology
EUS/EBUS for central lesions or nodal sampling
MRI brain if concern for metastases
LFTs – fitness for surgery
🚩Red Flags (2-Week Referral)
Refer if ≥40 with:
-
Haemoptysis
-
Persistent cough or breathlessness
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Chest pain
-
Hoarseness >3 weeks
-
Finger clubbing
-
Signs of mets (bone, neuro)
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – METASTATIC FEATURES
Bone pain
Neurological symptoms
Liver enlargement
Supraclavicular lymphadenopathy
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which clinical finding suggests metastatic lung cancer?
🧾 Management
🧠 Mnemonic: STAGE
Surgery – preferred for early-stage NSCLC
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – SCLC vs NSCLC
SCLC: aggressive, early spread, chemo/radio first-line
NSCLC: surgery possible if early-stage
SCLC is rarely surgical
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which type of lung cancer is usually not managed surgically?
Targeted therapy – if mutations (e.g. EGFR, ALK)
Anti-PD-1 immunotherapy (e.g. pembrolizumab)
Guided radiotherapy (SBRT) – non-surgical candidates
Etoposide + cisplatin – SCLC chemotherapy backbone
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLE
Early NSCLC → surgery offers best chance of cure
SCLC → chemotherapy ± radiotherapy
MDT involvement essential
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which lung cancer type is most likely to be treated surgically if detected early?
Palliative: chemo/radio, stents, pleurodesis for effusions, pain control
MDT involvement is essential at all stages
📌 PARA Revision Tips
Persistent cough + haemoptysis = CXR & 2WW
Know paraneoplastic syndromes → high yield
CT chest + PET + histology = gold standard
SCLC is NOT surgical — usually chemo/radio
NSCLC early = surgery best chance
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – RED FLAGS / 2WW
Haemoptysis in adults ≥40
Persistent cough or breathlessness
Unexplained weight loss
Hoarseness or supraclavicular nodes
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which symptom mandates an urgent 2-week cancer referral?
🧐Differential Diagnoses
🧠 Mnemonic: PENCIL
Pneumonia
Empyema
Non-malignant mass (e.g. hamartoma)
Cryptogenic organising pneumonia
Infectious granulomas (TB, fungal)
Lung abscess
🔎 Key PARA Exam Traps
💡 Persistent cough, weight loss, haemoptysis = lung cancer until proven otherwise
💡 Normal CXR does NOT exclude lung cancer: High suspicion → urgent CT chest
💡 Smoking is the strongest risk factor, but lung cancer occurs in non-smokers
💡 Hoarseness, Horner’s syndrome, arm pain → think Pancoast tumour
💡 Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is aggressive and rarely surgical
💡 Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) may be treated surgically if early stage
💡 SIADH, hypercalcaemia, Cushing’s = paraneoplastic syndromes (exam favourite)
💡 Supraclavicular lymphadenopathy strongly suggests malignancy
💡 Unexplained recurrent “pneumonia” in the same lobe → suspect obstruction by tumour
💡 Always consider metastatic disease: Bone pain, neurological symptoms, liver enlargement
🔎Last updated in line with NICE NG122 – Lung Cancer
Published: March 2019 • Last updated: February 2024
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
🔒PASSMAP ensures all content is NICE-aligned and reviewed for Physician Associate Registration Assessment (PARA) success.
