7. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
📄 Definition
IBD = Inflammatory Bowel Disease: chronic, relapsing inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, mainly Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Crohn’s Disease (CD).
🛡️ Aetiology / Risk Factors (exam-lean)
Immune dysregulation + genetics (NOD2 and others), microbiome changes
Smoking: ↑ risk/worse course in CD; often milder activity in UC if smoking (⚠️ never advise smoking)
Environmental: NSAIDs, antibiotics, Western diet; appendicectomy lowers UC risk
Family history; autoimmune associations (e.g., Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) in UC)
 Clinical Features
Clinical Features
| Feature | Ulcerative Colitis (UC) | Crohn’s Disease (CD) |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Continuous from rectum proximally (colon only) | Skip lesions, mouth→anus (often terminal ileum) |
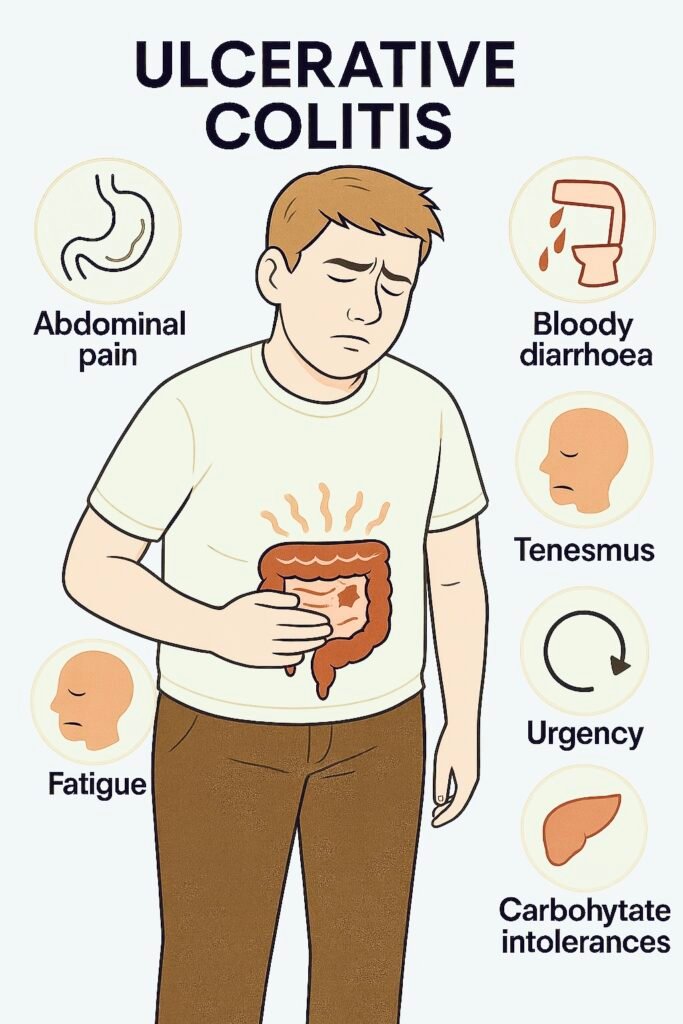
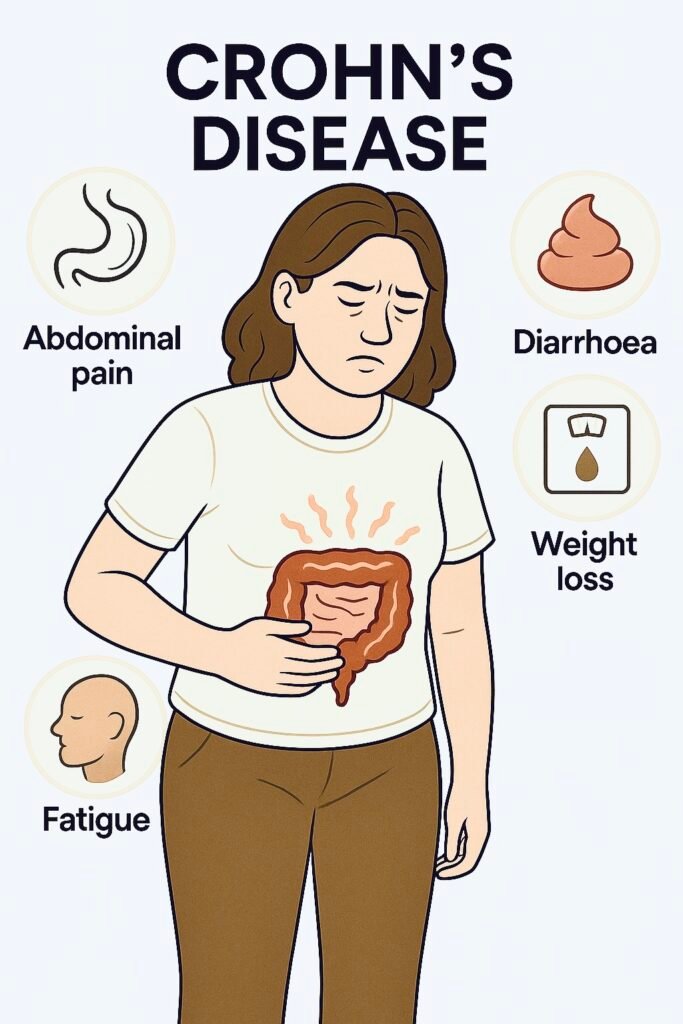
| Symptoms | Bloody diarrhoea, urgency, tenesmus (persistent, painful urge to defecate, despite an empty bowel) | Abdominal pain (RLQ common), weight loss, non-bloody diarrhoea |
| Rectal involvement | Almost always | Often spared |
| Perianal disease | Rare | Common (fissures, fistulae, abscess) |
| Exam/extra-intestinal | Pale (anaemia), tender colon; arthritis, erythema nodosum, uveitis, PSC | Tender RLQ, mass, scars; arthritis, erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum, uveitis |
🚩 Red Flags & When to Refer (IBD suspicion or known IBD)
| Tier | Key triggers (examples) | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 🚑 Immediate emergency | Toxic megacolon (severe systemic toxicity + colonic dilation >6 cm), suspected perforation, severe GI bleed, sepsis, uncontrolled pain/dehydration | Same-day ED/acute take; resuscitate; urgent surgical & GI review. |
| ⚡ Urgent gastroenterology | Raised faecal calprotectin (especially ≥250 µg/g), persistent diarrhoea >6 weeks with weight loss/anaemia, nocturnal symptoms, abnormal CRP/ESR | Urgent clinic; colonoscopy with biopsies ± small-bowel imaging. |
| 📮 Routine IBD service | Stable patients needing optimisation of maintenance therapy, vaccination review, surveillance planning | Community/specialist IBD pathway |
Faecal calprotectin (NICE DG11): supports IBD vs non-IBD. Practical pathway often uses <100 µg/g = IBS likely, 100–250 µg/g = repeat after stopping NSAIDs, >250 µg/g = refer. Use with clinical judgement.
🔬 Investigations (to confirm type & extent)
| Test | Why | Details / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| FBC, U&E, LFTs, CRP/ESR (full blood count; renal/liver panels; C-reactive protein / erythrocyte sedimentation rate) | Anaemia, inflammation, baseline safety | CRP tracks activity; check albumin (severity marker). |
| Stool tests | Exclude infection | Faecal calprotectin, C. difficile toxin, stool culture/ova-parasites as indicated. |
| Ileocolonoscopy + segmental biopsies | Gold standard to diagnose/classify | UC: continuous colitis; CD: patchy, ulcers, strictures, granulomas. |
| MR enterography (MRE) | Small-bowel CD activity/complications | Preferred over CT to limit radiation. |
| Pelvic MRI / EUA | Perianal CD | Map fistulae/abscess. |
| Surveillance colonoscopy (CRC prevention) | Dysplasia/cancer surveillance in colonic IBD | Begin ~8–10 years after symptom onset if colon involved; interval 1–5 years by risk (extent, activity, PSC). NICE CG118; BSG updated 2025. |
 Management — Stepwise Ladders (induction → maintenance)
Management — Stepwise Ladders (induction → maintenance)
A) Ulcerative Colitis (UC) — NICE NG130
Mild–moderate flare
5-ASA (mesalazine) topical ± oral (dose/form matched to extent).
If inadequate → add oral prednisolone (short course).
Proctitis only → rectal 5-ASA first; add rectal steroid if needed.
Maintenance
Continue 5-ASA to maintain remission; optimise adherence and formulation.
Acute Severe UC (ASUC) — admit
IV hydrocortisone, stool C. difficile, VTE (venous thromboembolism) prophylaxis, daily senior review, early flexible sigmoidoscopy (biopsy for CMV).
Day-3 non-response → rescue: infliximab or ciclosporin; urgent colorectal surgery input.
B) Crohn’s Disease (CD) — NICE NG129
Induction (by site/severity)
Oral prednisolone for moderate flares; budesonide for mild ileo-caecal disease.
Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) first-line in children/young people.
Consider azathioprine/mercaptopurine with steroid if ≥2 flares/yr or steroid-dependent. Aminosalicylates only if steroids contraindicated/declined (less effective).
Maintenance
Azathioprine/mercaptopurine (thiopurines) or methotrexate if thiopurines not tolerated/contraindicated.
Do not routinely use 5-ASA to maintain remission in CD.
Biologics / advanced therapies (specialist)
Anti-TNF (infliximab/adalimumab), vedolizumab, ustekinumab; JAK inhibitors in selected UC cases per TA/local formulary. Screen TB/HBV; update inactivated vaccines; avoid live vaccines on biologics.
Perianal CD
MRI pelvis, antibiotics if infected, drainage/seton if abscess/fistula; anti-TNF for complex disease. (Specialist pathway.)
Supportive Care (both UC & CD)
Nutrition: correct iron/B12/folate/vitamin D; consider dietitian; EEN in paediatrics.
Smoking cessation (especially CD).
Bone protection on repeated steroids; PPI if high GI-bleed risk.
Fertility/pregnancy: most 5-ASA/thiopurines/anti-TNF are compatible; seek specialist advice.
🔁 Follow-Up & Monitoring (primary–secondary care interface)
| Phase | Frequency | Core checks | Escalate if… |
|---|---|---|---|
| During flare / new Rx | 2–4 weeks | Symptoms, stool freq/bleeding, CRP, faecal calprotectin, weight, steroid side-effects | Non-response by 2–3 wks, rising markers, dehydration |
| Stable maintenance | 8–12 weeks, then 3–6 monthly | Activity indices, bloods (FBC, U&E, LFTs), drug monitoring (thiopurines/methotrexate), vaccination status | Steroid dependence, recurrent flares, adverse effects |
| Surveillance | Per CG118/BSG risk | Book colonoscopic surveillance per risk tier | New dysplasia, strictures, PSC → MDT |
🧠 Memory Boxes
UC vs CD: UC = continuous COLON + BLOOD; CD = skip lesions, ileum, weight loss, perianal.
ASUC shorthand: “IV steroid → Day-3 check → Rescue (IFX/CsA) → Surgery if failing”.
Calprotectin rules: <100 IBS likely; 100–250 repeat off NSAIDs; >250 refer.
Smoking: bad for Crohn’s, don’t recommend in UC.
Maintenance: UC → 5-ASA; CD → thiopurine/methotrexate (not 5-ASA).
 Last updated in line with
Last updated in line with
NICE NG129 – Crohn’s disease: management (children, young people, adults). Published May 2019; current online content.
NICE NG130 – Ulcerative colitis: management. Published May 2019; last reviewed 18 Feb 2025.
NICE DG11 – Faecal calprotectin (IBD vs non-IBD) with primary-care cut-offs.
NICE CG118 – Colonoscopic surveillance in IBD (CRC prevention; intervals by risk).
BSG 2025 guideline update for Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis (ASUC) (day-3 decision; rescue therapy)
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
