3.1. Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
📄 Definition
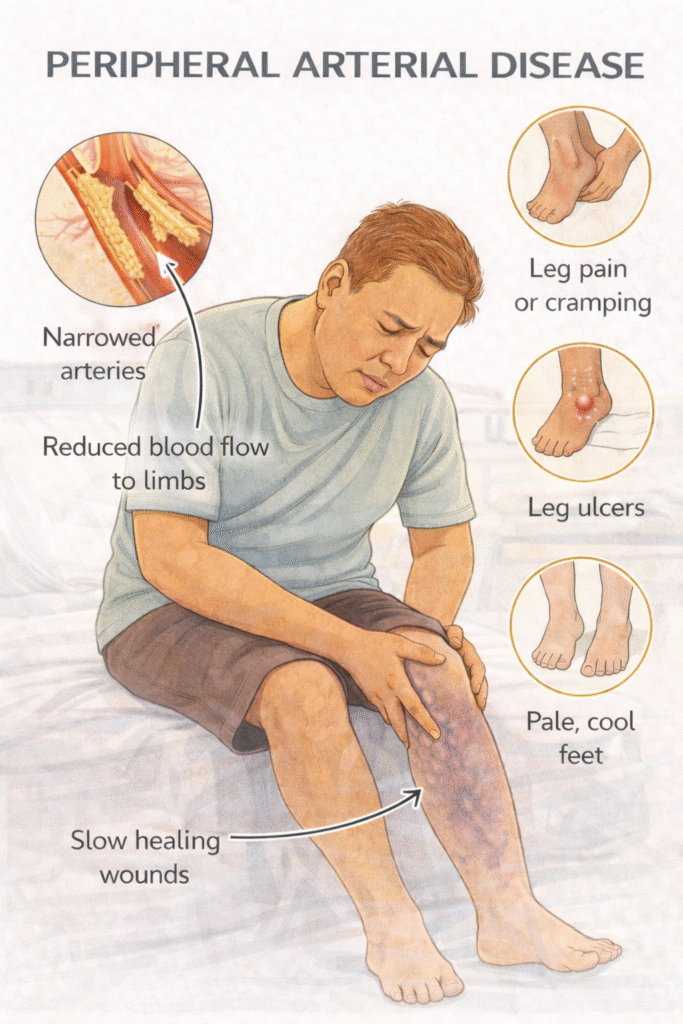
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a manifestation of systemic atherosclerosis causing stenosis or occlusion of arteries, primarily affecting the lower limbs. It ranges from asymptomatic disease to critical limb ischaemia.
⚠️ Classification
Asymptomatic PAD: reduced pulses, ABPI <0.9 but no symptoms
Intermittent Claudication: reproducible leg pain with exertion, relieved by rest
Critical Limb Ischaemia (CLI): chronic pain at rest, ulceration, or gangrene
🛡️ Risk Factors – Mnemonic: ATHEROSE
Age >60
Tobacco use (most significant modifiable)
Hypertension
Elevated cholesterol
Renal impairment (CKD)
Obesity
Sedentary lifestyle
Endocrine: Diabetes mellitus
Investigations
 First-Line
First-Line
ABPI (Ankle-Brachial Pressure Index):
<0.9 = diagnostic of PAD
<0.5 = severe disease
Duplex Doppler Ultrasound – assess blood flow and stenosis
 EXAM ANCHOR 1 – THE ABPI INTERPRETATION
EXAM ANCHOR 1 – THE ABPI INTERPRETATION
The Ankle-Brachial Pressure Index (ABPI) is your first-line diagnostic test.
Normal: 1.0 – 1.2
PAD: < 0.9
Critical Limb Ischaemia: < 0.5 (or ankle pressure < 50 mmHg)
PARA TRAP – The Calcified Vessel: In patients with Diabetes or CKD, arteries can become calcified and non-compressible. This leads to a falsely high ABPI (> 1.2). If you see a high ABPI in a symptomatic diabetic, the next step is a Toe-Brachial Pressure Index (TBPI) or Duplex Ultrasound.
 Second-Line
Second-Line
MR Angiography or CT Angiography – pre-intervention planning
Bloods: FBC, U&Es, HbA1c, Lipids, LFTs, ESR/CRP
ECG – evaluate cardiovascular risk
 Clinical Features –
Clinical Features –
Mnemonic: 6 Ps (acute) and CLAUDICATE (chronic)
Acute Limb Ischaemia – 6 Ps:
Pain
Pallor
Pulselessness
Paralysis
Paraesthesia
Perishing cold
Chronic PAD – Mnemonic: CLAUDICATE
Cramping calf pain
Loss of hair
Abnormal pulses
Ulcers (arterial)
Dry, shiny skin
Intermittent claudication
Cool peripheries
ABPI <0.9
Toe pallor
Erectile dysfunction (Leriche syndrome)
 EXAM ANCHOR 1 – CHRONIC VS. ACUTE FEATURES
EXAM ANCHOR 1 – CHRONIC VS. ACUTE FEATURES
Intermittent Claudication: Pain is reproducible (occurs at the same distance every time) and relieved by rest.
Critical Limb Ischaemia (CLI): Defined by the “Triad of Trouble”:
Rest Pain: Burning pain at night, relieved by hanging the leg over the edge of the bed (gravity helps perfusion).
Ulceration: Typically “punched out” ulcers on the toes or heels.
Gangrene.
Management – Mnemonic: PAD CARE
Prevention – smoking cessation, weight reduction, exercise
Antiplatelet – clopidogrel first-line
Dual risk factor control – manage BP, lipids, diabetes
Cilostazol (for symptom relief in intermittent claudication)
Angioplasty or stenting – severe symptoms or CLI
Revascularisation – surgical bypass if angioplasty not feasible
Education – foot care, PAD risk understanding
 EXAM ANCHOR 1 – MANAGEMENT (NICE CG147)
EXAM ANCHOR 1 – MANAGEMENT (NICE CG147)
The PARA tests your ability to prioritize medical management before jumping to surgery.
- Antiplatelet: Clopidogrel 75mg is the first-line choice (Aspirin is second-line for PAD).
- Statin: Atorvastatin 80mg (High-intensity) for all patients.
- Supervised Exercise Programme: This is the first-line non-drug treatment for intermittent claudication. Patients should walk until the pain is near-maximal, then rest, then repeat for 30–45 mins, 3x per week.
- Naftidrofuryl oxalate: If exercise and risk factor modification fail, this can be offered for symptom relief (NICE alternative to Cilostazol).
⚠️ Complications
Critical limb ischaemia
Amputation
Ulceration
Cardiovascular morbidity (MI, stroke)
🔎 Key PARA Exam Traps
Buerger’s Test: Raising the leg causes it to go pale (pallor), and lowering it causes it to turn a deep red (reactive hyperaemia). This is a classic sign of severe ischaemia.
Foot Care: Diabetic patients with PAD need referral to a Podiatrist. Even a small nick during a nail trim can lead to a non-healing ulcer and amputation.
Beta-Blockers: There is an old myth that Beta-blockers are contraindicated in PAD. NICE states they are safe to use if needed for other conditions, though they may rarely worsen symptoms in some patients.
🔺 Last updated in line with NICE CG147 – Peripheral arterial disease: diagnosis and management
Published: August 2012 • Last updated: October 2020
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
✅ PASSMAP ensures all content is NICE-aligned and reviewed for Physician Associate Registration Assessment (PARA) success.
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
