7.1. Infective Endocarditis
📄 Definition
Infective endocarditis (IE) is an infection of the endocardial surface of the heart, typically involving the heart valves. It is a life-threatening condition requiring prompt diagnosis and treatment.
🧪 Causative Organisms – Mnemonic: SHAVE
Staphylococcus aureus – most common overall (especially in IVDU)
HACEK organisms – Gram-negative (Haemophilus, Aggregatibacter, Cardiobacterium, Eikenella, Kingella)
Alpha-haemolytic Streptococci (Viridans group) – dental link
Valvular prostheses – ↑ risk of coagulase-negative staph (e.g. S. epidermidis)
Enterococci – linked with GI or GU procedures
⚠️ Risk Factors
Prosthetic heart valves
Intravenous drug use (IVDU)
Structural heart disease (e.g. bicuspid aortic valve, mitral valve prolapse)
Previous IE
Indwelling catheters or invasive procedures (dental/GI)
📋 Clinical Features – Mnemonic: FROM JANE
Fever (most common)
Roth spots (retinal haemorrhages with pale centre)
Osler nodes (painful fingertip nodules – immune complex)
Murmur (new or changing)
Janeway lesions (painless palm/sole macules – septic emboli)
Anaemia of chronic disease
Nail-bed (splinter) haemorrhages
Emboli – e.g. stroke, PE, renal infarcts
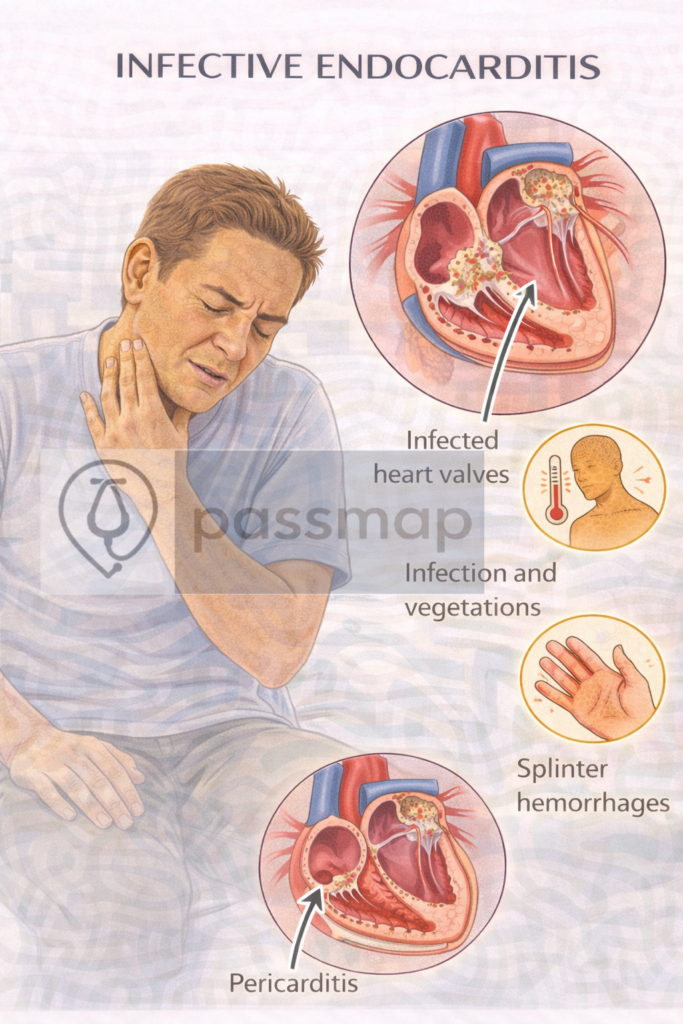
🧠 Diagnosis – Modified Duke Criteria
🔹 Major Criteria:
Positive blood cultures (e.g. typical organisms in 2 separate samples)
Endocardial involvement on echocardiogram (vegetation, abscess, new regurgitation)
🔸 Minor Criteria:
Predisposing heart condition or IVDU
Fever ≥38°C
Vascular phenomena (Janeway, emboli)
Immunologic phenomena (Osler, Roth, GN, RF+)
Positive cultures not meeting major criteria
✅ Diagnosis: 2 major, or 1 major + 3 minor, or 5 minor
🔬 Investigations – Tiered Approach
🥇 First-Line:
3 sets of blood cultures (at least 1 hour apart, different sites)
FBC, U&Es, LFTs, CRP/ESR
ECG – baseline for comparison
Transthoracic Echo (TTE)
🥈 Second-Line:
Transoesophageal Echo (TOE) – more sensitive
Urinalysis – haematuria (immune complex GN)
CXR – pulmonary emboli or signs of heart failure
🥉 Special Tests:
Serology – Coxiella, Bartonella (culture-negative IE)
Rheumatoid factor
Autoantibodies (ANA, ANCA)
Management – Mnemonic: BITE
Blood cultures (before antibiotics)
Initiate empiric IV antibiotics (e.g. amoxicillin + gentamicin)
→ adjust per microbiologyTOE to confirm vegetations
Escalate to cardiology/cardiothoracics if:
Persistent infection
Severe valve dysfunction/heart failure
Embolic risk
Prosthetic valve involvement
🔒 NICE NG183 advises 4–6 weeks IV antibiotics based on microbiology.
❗ Complications – Mnemonic: HEART
Heart failure (valve destruction)
Embolic events (stroke, spleen, kidney, lung)
Abscesses (myocardial, perivalvular)
Renal damage (GN, infarcts)
Total valve destruction → surgery
🦷 Prevention
Good dental hygiene
Antibiotic prophylaxis only in high-risk patients undergoing invasive dental procedures:
Prosthetic valves
Previous IE
Congenital heart disease (unrepaired or repaired with prosthesis)
🔺 Last updated in line with NICE NG183 – Endocarditis (antimicrobial prescribing)
Published: November 2020 • Last updated: January 2023
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
✅ PASSMAP ensures all content is NICE-aligned and reviewed for Physician Associate Registration Assessment (PARA) success.
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
