1. Heart Failure (Acute and Chronic)
📄 Definition
Heart failure (HF) is a clinical syndrome caused by structural/functional cardiac abnormality → impaired ventricular filling or ejection → inadequate cardiac output and/or raised intracardiac pressures.
Acute HF: rapid onset/worsening of symptoms (often pulmonary oedema).
Chronic HF: persistent symptoms, usually stable with periods of decompensation.
Pathophysiology
↓ Cardiac output → ↑ Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS) and Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS) → fluid retention, vasoconstriction, remodelling
HFrEF = systolic failure
HFpEF = diastolic dysfunction
🛡️ Classification
| Category | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| By LVEF | – HFrEF: reduced EF ≤40% – HFmrEF: mildly reduced EF 41–49% – HFpEF: preserved EF ≥50% | NICE/ESC use echo EF cut-offs |
| By presentation | Acute vs chronic | Acute = pulmonary oedema, cardiogenic shock |
| By sidedness | Left vs right vs biventricular | Right HF often secondary to left HF or lung disease (cor pulmonale) |
 Risk Factors
Risk Factors

-
Diabetes
-
Age
-
Myocardial infarction
-
NSAIDs/nephrotoxins
-
Hypertension
-
Ethanol
-
Arrhythmias
-
Renal dysfunction
-
Thyroid disease
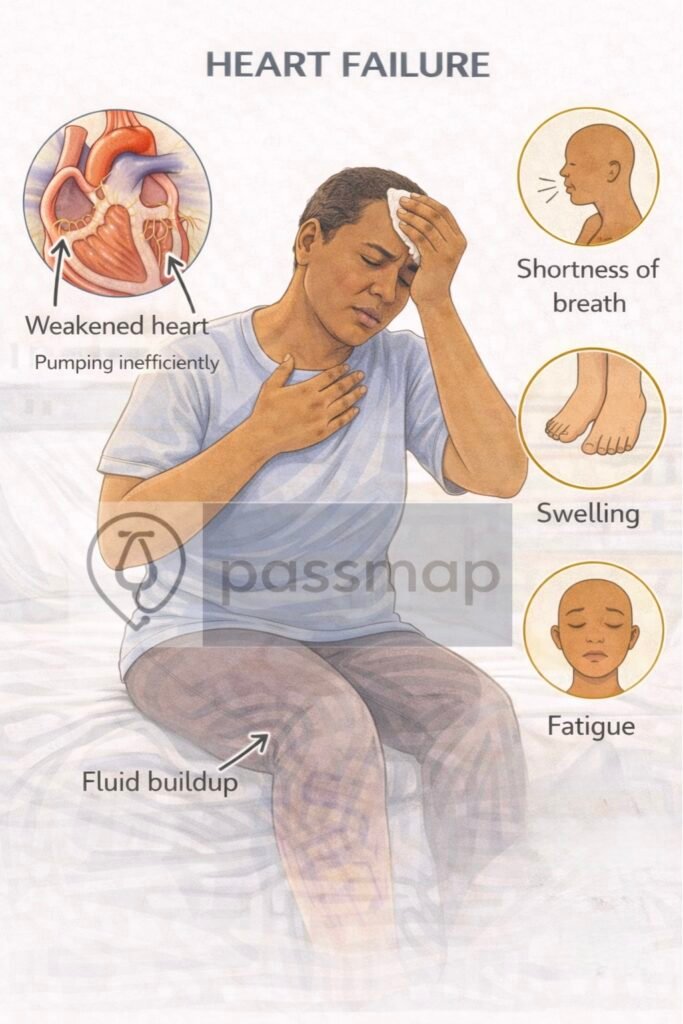
🤒 Clinical Features (Mnemonic: FAILURE)
Fatigue, reduced exercise tolerance
Anxiety, nocturia
Increased JVP
Lung crackles, orthopnoea, PND (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea)
Unsure pulse (AF common)
Rales (basal crackles), peripheral oedema
Exertional breathlessness
Acute HF: severe breathlessness, orthopnoea, pink frothy sputum, tachycardia, clammy peripheries.
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – SIDEDNESS
Left-sided HF → pulmonary congestion
Bilateral basal crackles
Orthopnoea / Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea
Right-sided HF → systemic venous congestion
Raised JVP
Peripheral oedema
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which clinical sign is most associated with left-sided heart failure?
🚩 Red Flags / Admit if
Pulmonary oedema, hypoxia, hypotension.
Cardiogenic shock (SBP <90, poor perfusion).
Rapidly rising creatinine/oliguria.
New arrhythmia or ACS trigger.
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – ADMISSION
Pulmonary oedema
Cardiogenic shock
Hypotension or hypoxia
📌 PARA often frames these as:
“Which patient requires urgent admission?”
🔬 Investigations (Stepwise PARA Focus)
| Step | Test | Findings / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Initial | BNP/NT-proBNP | High level supports HF; normal makes HF unlikely. BNP >400 pg/mL → 2-week echo; >2000 pg/mL → 2-day echo. |
| FBC, U&E, LFTs, TFTs, glucose, lipids | Look for anaemia, renal dysfunction, thyroid, DM, risk factors. | |
| CXR | Cardiomegaly, pulmonary oedema, Kerley B lines. | |
| 2️⃣ Diagnostic | Echocardiography | Essential to confirm LV function and classify (HFrEF, HFpEF). |
| 3️⃣ Additional | ECG (arrhythmias, ischaemia), troponin (exclude ACS), iron studies (HF can be worsened by iron deficiency). |
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – BNP
Normal BNP → heart failure very unlikely
High BNP triggers urgent echo
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which test is most useful to rule out heart failure?
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – DIAGNOSIS
Echocardiogram = diagnostic gold standard
Required to classify HFrEF vs HFpEF
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which investigation confirms the diagnosis of heart failure?
CXR FINDINGS
 Mnemonic: ABCDE
Mnemonic: ABCDE
Alveolar oedema (bat-wing)
Basal effusions
Cardiomegaly
Dilated upper lobe veins
Effusions (interlobar)
Severity – NYHA Classification
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| I | No limitation |
| II | Mild limitation |
| III | Marked limitation |
| IV | Symptoms at rest |
📋 Management
A) Acute Heart Failure (NICE / ESC)
| Step | Treatment | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Immediate | Sit upright, high-flow O₂ if hypoxic, monitor (SpO₂, ECG, BP). | Avoid O₂ if sats normal. |
| 2️⃣ Loop diuretics | IV furosemide (40–80 mg). | First-line for pulmonary oedema. |
| 3️⃣ Vasodilators | IV nitrates if SBP >100 mmHg. | Avoid if hypotensive/severe AS. |
| 4️⃣ Inotropes | Dobutamine/NA if cardiogenic shock. | Specialist/ICU setting. |
| 5️⃣ Treat cause | ACS, arrhythmia, infection, PE, non-adherence. |
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – ACUTE HF
First-line drug in pulmonary oedema = IV loop diuretic
Treat the trigger (ACS, arrhythmia, infection)
📌 PARA commonly asks:
First-line treatment in acute pulmonary oedema?
B) Chronic Heart Failure (HFrEF – reduced EF ≤40%)
Stepwise ladder (NICE NG106 2026):
1️⃣ The goal is Rapid Sequence Initiation: all four pillars should be started within 4–6 weeks of diagnosis.
| Pillar | Medication | 2026 NICE Guidance |
| 1 | ACEi or ARNI | Ramipril (ACEi) is traditional, but Sacubitril/Valsartan (ARNI) is now recommended if symptoms persist on ACEi or can be started de novo in hospital. |
| 2 | Beta-Blocker | Bisoprolol or Carvedilol. Start low but do not wait for “target dose” before adding other pillars. |
| 3 | MRA | Spironolactone or Eplerenone. Introduced early (Pillar 3) to reduce mortality and remodeling. |
| 4 | SGLT2i | Dapagliflozin or Empagliflozin. Now a first-line “Big Four” drug for all HFrEF, regardless of diabetes status. |
Screening: Check Ferritin and TSAT for all HF patients at diagnosis and at every 6-month review.
Treatment: If Ferritin <100 µg/L (or 100–299 if TSAT <20%), offer IV Iron (e.g., Ferric Derisomaltose).
Note: Oral iron is generally ineffective in heart failure due to poor absorption; IV is the standard for reducing hospitalizations.
C) HFpEF (Preserved Ejection Fraction ≥50%)
The “no treatment” era is over. Management is now proactive.
First-Line Therapy: SGLT2 inhibitors (Dapagliflozin or Empagliflozin) are now the only drugs proven to reduce CV death and hospitalizations in HFpEF.
Second-Line (Consider): MRAs (Spironolactone) are now recommended by NICE to be considered for symptom control and reducing admission risk.
Congestion: Use loop diuretics (Furosemide) as needed for fluid status.
Aggressive Comorbidity Management:
BP Control: Aim for <130/80 mmHg.
AF: High priority for rate/rhythm control (stiff hearts rely on the “atrial kick”).
Weight: Weight loss is a formal therapeutic goal to improve exercise tolerance.
🩺 3. Monitoring & Titration (The 2026 Checklist)
Because multiple drugs affecting the RAAS and kidneys are started quickly, monitoring is more frequent:
Frequency: Monitor U&Es (Potassium/Creatinine) every 1–2 weeks during initiation/titration, then 6-monthly when stable.
Acceptable Shifts:
Creatinine: A rise of up to 30% is acceptable (do not stop the drug unless >50%).
Potassium: Aim to keep <5.5 mmol/L. If it hits 6.0 mmol/L, stop the MRA/ACEi and review.
The “36-Hour Rule”: If switching from an ACEi to an ARNI, you must wait 36 hours between the last ACEi dose and the first ARNI dose to prevent life-threatening angioedema.
Quick Summary Table for Exams
| If the patient has… | The “Best Next Step” is… |
| New Diagnosis | Start ACEi/ARNI + Beta-blocker (+ SGLT2i/MRA ASAP). |
| Symptoms on ACEi | Switch to ARNI (Wait 36 hours!). |
| Persistent Congestion | Increase Loop Diuretic (Furosemide). |
| Fatigue + Low Ferritin | IV Iron (Not oral). |
| HFrEF + HR >75bpm + Sinus Rhythm | Consider Ivabradine. |
🩺 Monitoring
Weight (target: <2kg/week loss)
Monitor U&Es on ACEi/MRA
Echo every 1–2 years
Digoxin monitoring if used
Annual flu + 1-off pneumococcal vaccine
 Complications
Complications
🧠 Mnemonic: CHAD
Cardiogenic shock
Hypokalaemia / hyponatraemia
Arrhythmias
Death (sudden cardiac)
🔎 Key PARA Exam Traps
💡 BNP normal → HF very unlikely.
💡 Echo = diagnostic gold standard.
💡 SGLT2 inhibitors are now standard therapy for HFrEF.
💡 Loop diuretics improve symptoms but NOT survival.
💡 Always look for & treat reversible causes (ACS, valve disease, thyroid, arrhythmias, anaemia).
📅Last updated in line with:
NICE NG106 (2025/26 Update): Reflecting Rapid Sequence Initiation for the Four Pillars.
NICE TA902 & TA929 (2023/24): Formally mandating SGLT2 inhibitors (Dapagliflozin/Empagliflozin) for HFpEF and HFmrEF.
ESC HF Guidelines (2023 Focused Update): Regarding the management of acute decompensation and iron deficiency.
UK Kidney Association (2024): Guidelines on potassium and creatinine tolerance during RAAS-inhibitor initiation.
PARA/MLA-aligned: Reviewed February 2026 for the current exam cycle.
🔒 PASSMAP Assurance: All content is peer-reviewed, NICE-compliant, and optimized for the GMC Medical Licensing Assessment (MLA) and PA National Exam (PARA).
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
