Arrhythmias are abnormal heart rhythms resulting from disturbances in the generation or conduction of electrical impulses within the heart. They may be:
Tachyarrhythmias (HR >100 bpm)
Bradyarrhythmias (HR <60 bpm)
Irregular (e.g. atrial fibrillation)
Regular but abnormal (e.g. SVT, VT)
📊 Classification
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Supraventricular | AF, Atrial flutter, SVT, AVNRT, WPW |
| Ventricular | VT, VF, PVCs |
| Bradyarrhythmias | Sinus bradycardia, AV blocks |
| Irregular rhythms | AF, ectopics |
🔍 Causes
🧠 Mnemonic: HIS DEATH
Hypoxia
Ischemia (MI)
Stimulants (caffeine, cocaine)
Drugs (e.g. digoxin, beta-blockers, antiarrhythmics)
Electrolyte imbalance (K+, Mg²⁺)
Anaemia
Thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
Heart disease (HF, valvular, cardiomyopathy)
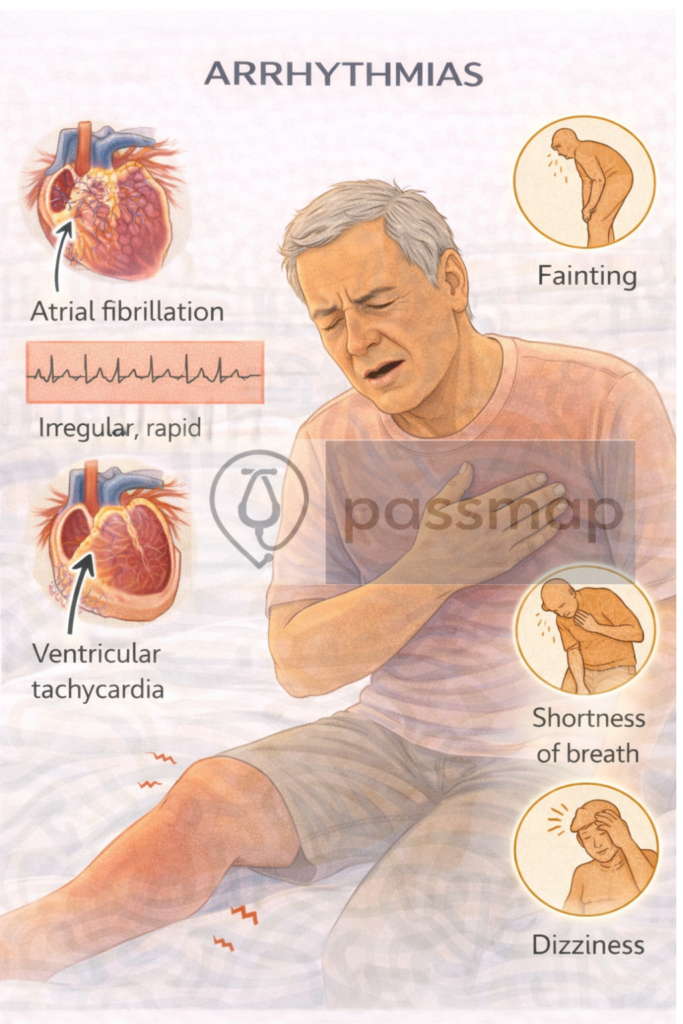
📋Clinical Features
Palpitations
Dizziness, syncope
Chest pain
Dyspnoea
Fatigue
Sudden cardiac death (in VT/VF)
📈 Diagnosis
🔹 ECG
AF: Irregularly irregular, no P waves
Atrial flutter: Sawtooth flutter waves
SVT: Regular narrow QRS tachycardia, often sudden onset/offset
VT: Broad complex tachycardia, AV dissociation
Bradycardia/AV block: PR prolongation, dropped beats
🔹 Other tests:
24-hour Holter monitor (intermittent arrhythmias)
Echocardiogram (structural heart disease)
TFTs, U&Es, Mg²⁺, Ca²⁺
Troponin (if ACS suspected)
Consider ILR (Implantable Loop Recorder) if unexplained syncope
⚡️ Supraventricular Arrhythmias
Atrial Fibrillation (AF)

Most common sustained arrhythmia
Irregularly irregular rhythm, no P waves
Risk of stroke: use CHA₂DS₂-VASc score
Anticoagulation if ≥2 (men) or ≥3 (women)
🧠 Mnemonic: ABC for AF
Anticoagulate
Beta-blocker or rate control
Cardioversion (electrical or pharmacological)
Rate vs Rhythm Control:
Rate: 1st line for most (BB, CCB, digoxin)
Rhythm: Younger, symptomatic, 1st episode (flecainide, amiodarone, cardioversion)
Atrial Flutter
Similar management to AF
Sawtooth ECG pattern
More amenable to ablation
SVT (AVNRT/AVRT)
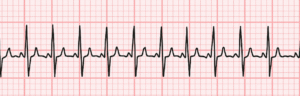
Sudden onset palpitations, regular narrow complex tachycardia
Management:
Vagal manoeuvres (1st line)
Adenosine IV (2nd line) – brief asystole
Long-term: BB, CCB, ablation
Ventricular Arrhythmias
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Broad QRS tachycardia (>3 consecutive PVCs)
Can be monomorphic or polymorphic
May progress to VF
Management:
Stable: Amiodarone IV
Unstable: DC shock
Long-term: implantable defibrillator
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF)
Chaotic electrical activity, no cardiac output
Cardiac arrest – immediate defibrillation (ALS protocol)
Bradyarrhythmias
Sinus Bradycardia

Often benign (athletes, sleep)
Treat if
symptomatic (e.g. dizziness, syncope)
Heart Block
| Type | ECG Features | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1st degree | PR >200 ms | Usually benign |
| 2nd degree I | Progressive PR prolongation → dropped beat | Mobitz I (Wenckebach) |
| 2nd degree II | Dropped beat with constant PR | Mobitz II → risk of asystole |
| 3rd degree | Complete dissociation (P ≠ QRS) | Requires pacing |
(ALS protocol)
Management Summary
| Situation | Management |
|---|---|
| AF | Anticoagulate + rate/rhythm control |
| SVT | Vagal → Adenosine → consider ablation |
| VT (stable) | Amiodarone |
| VT/VF (arrest) | Defibrillation + ALS |
| Bradycardia/block (symptomatic) | Atropine → pacing |
📋 Risk Tools & Scoring
CHA₂DS₂-VASc – Stroke risk in AF
HAS-BLED – Bleeding risk with anticoagulation
ESC 2020 guidelines for arrhythmia management
📦 Drugs to Know
| Drug | Use | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Adenosine | SVT | Brief asystole, warn patient |
| Amiodarone | VT, rhythm control in AF | QT prolongation, thyroid/lung/liver toxic |
| Beta-blockers | Rate control, SVT, VT | Avoid in asthma |
| Digoxin | AF (esp. with HF) | Narrow therapeutic window |
| Flecainide | Rhythm control | Avoid in structural heart disease |
🚩Red Flags to Escalate
Syncope or collapse
Broad complex tachycardia
Bradycardia with hypotension
Any arrhythmia with chest pain or breathlessness
Suspected long QT or family history of sudden death
PARA Clinical Competencies
ECG interpretation: AF, flutter, SVT, VT, heart block
Recognise unstable rhythms and escalate immediately
Understand prescribing: anticoagulants, rate/rhythm control
Safety net and counsel patients (e.g. driving restrictions in blackouts)
Know when to refer for cardiology or pacing
Last updated in line with NICE NG196 (Atrial fibrillation) and NICE CG180 (Palpitations and arrhythmias):
NG196 published April 2021, last updated April 2023
CG180 published June 2014, last updated November 2021
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
PassMap ensures all content is NICE-aligned and reviewed for PARA success.
Educational platform. Not medical advice.


