3.2 Ischaemic stroke – Cerebral artery thrombosis
📄 Definition
Ischaemic Stroke: Focal brain infarction with symptoms lasting >24 hours.
TIA: Neurological deficit resolving within 24 hours. (Note: Most TIAs actually resolve within 1 hour).
🧠 Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA): Neurological symptoms resolve within <24 hours and no infarction seen on imaging.
🧠 Causes – Mnemonic: THROMBO
Thromboembolism (from carotids or heart, e.g. AF)
Hypertension
Risk factors: smoking, diabetes, hyperlipidaemia
Oral contraceptives (young women)
Mural thrombus post-MI
Blood disorders (e.g. polycythaemia)
Other: carotid dissection, vasculitis
 EXAM ANCHOR – ANATOMY TRAPS
EXAM ANCHOR – ANATOMY TRAPS
MCA (Middle Cerebral): Most common. Affects the Face and Arm more than the Leg. Includes Aphasia (if dominant hemisphere).
ACA (Anterior Cerebral): Rare. Affects the Leg more than the Arm.
POCI (Posterior): Think Ataxia and Cranial Nerve palsies. If they mention “Crossed signs” (Face one side, body the other), it’s always a Brainstem/Posterior stroke.
 EXAM ANCHOR – IDENTIFYING THE SOURCE (THROMBO)
EXAM ANCHOR – IDENTIFYING THE SOURCE (THROMBO)
The PARA exam will often give you a cause from your THROMBO list and ask for the “Next Investigation” to prove it.
AF (Thromboembolism): If the pulse is irregular, the next step is an ECG or 24-hour Holter.
Carotids (Thromboembolism): If a carotid bruit is heard, the next step is Carotid Doppler Ultrasound.
Mural Thrombus (Post-MI): If the patient has a history of a large anterior MI, the next step is an Echocardiogram.
Oral Contraceptives: If the patient is a young female smoker on the pill, they are at high risk for both arterial stroke and Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis (CVST).
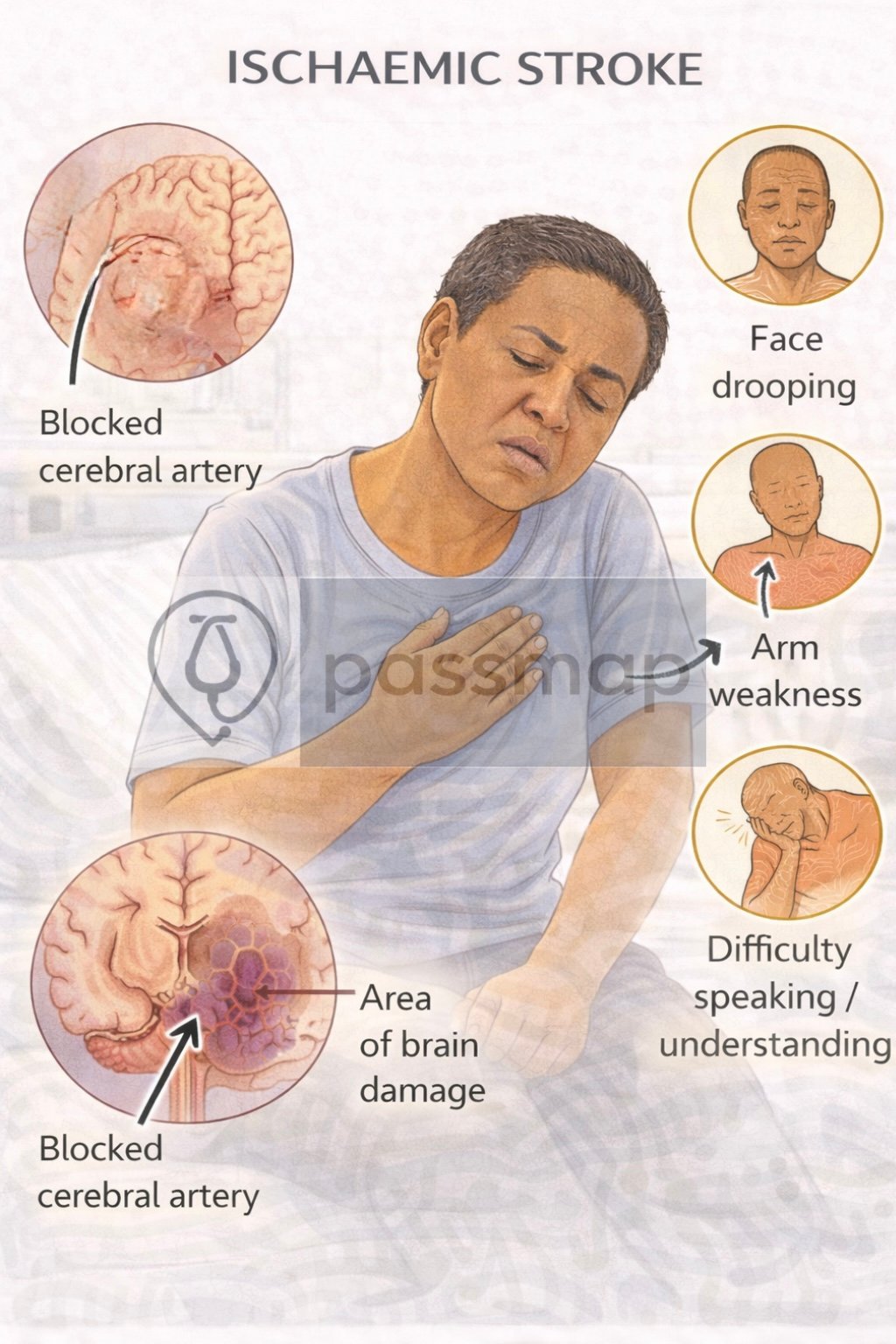
 Symptoms – FAST + others
Symptoms – FAST + others
-
Face drooping
-
Arm weakness
-
Speech disturbance
-
Time (act quickly)
-
Visual loss (amaurosis fugax, homonymous hemianopia)
-
Ataxia, vertigo (posterior circulation)
-
Dysphagia
-
Confusion or altered mental status
 EXAM ANCHOR – THE STROKE “MIMIC”
EXAM ANCHOR – THE STROKE “MIMIC”
Before CT or any intervention, you must perform a Capillary Blood Glucose.
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Hypoglycaemia can present with focal neurological deficits (hemiparesis/slurred speech) and is the most common stroke mimic.
 First-Line (Immediate)
First-Line (Immediate)
ABCDE assessment
Blood glucose – rule out hypoglycaemia mimic
Urgent CT Head (within 1 hour) – exclude haemorrhage
ECG – AF or MI
FBC, U&Es, LFTs, Clotting, CRP, Lipids, HbA1c
 THE ACUTE EMERGENCY
THE ACUTE EMERGENCY
Safety First: Capillary Blood Glucose (Rule out hypoglycemia).
Imaging: Non-contrast CT Head within 1 hour.
Treatment Windows:
Alteplase: <4.5 hours.
Thrombectomy: <6 hours (Large Vessel Occlusion).
Aspirin 300mg: Immediately after CT (unless thrombolysed, then wait 24h).
 Investigations
Investigations
 Second-Line
Second-Line
CT Angiography (CTA) – assess large vessel occlusion
Carotid Doppler US – check for stenosis
MRI Brain – more sensitive for posterior strokes
 EXAM ANCHOR – SECONDARY PREVENTION TITRATION
EXAM ANCHOR – SECONDARY PREVENTION TITRATION
Immediate: Give Aspirin 300 mg stat (unless anticoagulated or bleeding disorder).
Referral: All TIAs must be seen by a specialist within 24 hours.
Driving: Advise the patient not to drive until cleared by a specialist.
📌 PARA commonly asks:
A patient had a 10-minute episode of slurred speech 4 hours ago. They are now back to normal. What is the next step?”
 Tertiary
Tertiary
Echocardiogram – embolic source
24h Holter – paroxysmal AF
Thrombophilia screen – if <50 or unexplained stroke
Management – Mnemonic: ACT FAST
Antiplatelet – 300 mg aspirin STAT after haemorrhage excluded
CT Head – done urgently
Thrombolysis – alteplase IV within 4.5 hrs (if criteria met)
Fibrinolysis contraindicated? → consider thrombectomy (within 6 hours)
Antihypertensives – only if BP >185/110 mmHg
Statin – atorvastatin 80 mg after 48 hrs
TIA: refer to stroke clinic within 24 hours
 EXAM ANCHOR – ACUTE MANAGEMENT WINDOWS
EXAM ANCHOR – ACUTE MANAGEMENT WINDOWS
Management is dictated entirely by the time from symptom onset.
CT Head: Perform immediately (ideally within 1 hour) to exclude intracranial haemorrhage.
Thrombolysis (Alteplase): Administer within 4.5 hours.
Thrombectomy: Offer within 6 hours for confirmed large vessel occlusion (LVO). Can be considered up to 24 hours if there is salvageable brain tissue on advanced imaging.
Aspirin 300 mg: Give only after haemorrhage is excluded on CT.
Note: If thrombolysis is given, delay Aspirin for 24 hours.
Secondary Prevention (LONG-TERM)
1st Line: Clopidogrel 75mg + Atorvastatin 80mg.
AF-Stroke: Start DOAC after 14 days.
Carotid Stenosis (>50%): Refer for Endarterectomy within 14 days.
Driving: 1 month ban for both Stroke and TIA.
Complications – Mnemonic: BE FAST
Brain oedema
Embolism recurrence
Falls
Aspiration pneumonia
Seizures
TIA or progression to haemorrhagic stroke
 EXAM ANCHOR – THE “SAFETY CHECKS”
EXAM ANCHOR – THE “SAFETY CHECKS”
The PARA will often present a patient who could have thrombolysis but has a hidden contraindication.
You must NOT thrombolyse if:
Blood Pressure: >185/110 mmHg (Must lower safely before starting).
Glucose <2.8 or >22.2 mmol/L.
Surgery/Trauma within last 21 days.
Anticoagulated (INR >1.7 or on DOAC).
The “Permissive Hypertension” Rule
This is the most common trap in PARA finals.
The Rule: In a standard ischemic stroke, we do not lower the blood pressure (BP) acutely unless it is dangerously high (typically >220/120 mmHg).
The Reason: The brain tissue surrounding the dead zone (called the Penumbra) is struggling for life. Lowering the BP too quickly reduces “perfusion pressure,” which can turn salvageable brain tissue into a permanent infarct (dead tissue).
🔎 Key PARA Exam Traps
💡 The “Next Step” post-CT: If the CT shows no blood and the patient is within 4.5 hours, the next step is Thrombolysis, not Aspirin.
💡 Posterior Circulation: If the symptoms are vertigo, ataxia, or “locked-in” syndrome, the lesion is in the Basilar Artery/Posterior circulation. CT is often normal; MRI is the investigation of choice here.
💡 Carotid Endarterectomy: Offered if there is >50% stenosis (symptomatic) and the patient is fit for surgery. This should be done within 14 days of the stroke/TIA.
💡 AF Source: If the stroke was caused by AF, do not use Clopidogrel. Use a DOAC (started 14 days after the stroke).
🔒 Last updated in line with:
NICE NG128 (Stroke and TIA: 2019, updated 2022/23).
Last reviewed: February 2026.

Educational platform. Not medical advice.
