3.1 Myocardial Infarction (MI) – Coronary Artery Thrombosis
📘 Cross-reference: [See Section 2 – Acute Coronary Syndromes (ACS)] https://passmap.co.uk/cardiology-1-acute-coronoary-syndromes/ for full clinical approach, ECG patterns, biomarkers, and guideline-driven management.
📄 Definition
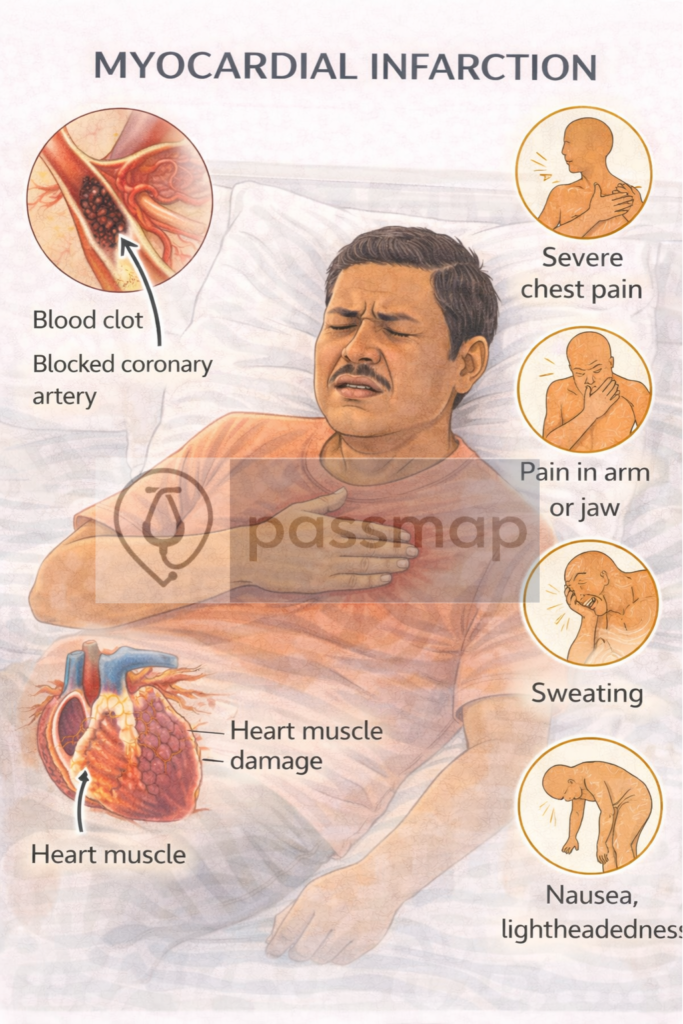
Myocardial infarction (MI) is myocardial necrosis due to acute thrombotic occlusion of a coronary artery. It is a clinical manifestation of arterial thrombosis and a common cause of sudden cardiac death.
🧠 PASSMAP Integration
This condition is the archetype of arterial thrombosis and integrates with systemic atherosclerosis. Recognising shared risk factors with PAD, stroke, and acute limb ischaemia is high-yield for PARA success.
🔬 Pathophysiology
Triggered by rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque in a coronary artery.
Results in platelet aggregation and formation of a white thrombus in high-pressure arterial flow.
Thrombus partially or completely occludes the coronary artery:
Partial occlusion → NSTEMI
Complete occlusion → STEMI
Leads to ischaemia, hypoxia, and myocyte death.
⚠️ Risk Factors – Mnemonic: THROMBUS
Tobacco use
Hypertension
Raised lipids
Obesity
Male sex / Metabolic syndrome
Blood glucose (diabetes mellitus)
Unhealthy diet / sedentary lifestyle
Stress / psychosocial factors
🩺 Red Flag Signs (pre-hospital recognition)
Crushing central chest pain ± radiation to arm/jaw
Sweating, nausea, breathlessness
Syncope or hypotension
Sudden collapse or cardiac arrest
🧪 Investigations
✅ Full workup found in Section 2 (ACS), but key mechanistic markers include:
Troponin T or I – indicates myocardial necrosis
ECG – ST elevation (STEMI) or T wave changes/ST depression (NSTEMI)
Coronary angiography – to confirm thrombotic occlusion
💡 Did You Know? Type 1 vs. Type 2 MI
While both present with a rise and/or fall in Troponin and symptoms of ischaemia, the “Type” refers to the underlying mechanism, which fundamentally changes the management plan.
Type 1 MI: The “Clot” Problem
This is the “classic” heart attack where the problem is a physical blockage in the blood vessels of the heart.
A – Acute: Rapid onset of symptoms.
C – Clot: Formation of a Thrombus (blood clot).
D – Disruption: Rupture or erosion of an Atherosclerotic Plaque (fatty buildup in the artery wall).
C – Coronary: Specifically involving the Coronary Arteries (the vessels that supply the heart muscle).
Mechanism: Acute atherothrombosis. A plaque ruptures, a thrombus forms, and the artery is blocked.
Key Feature: This is your classic Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS).
Management: Reperfusion (PCI), DAPT, and aggressive secondary prevention (The 6 As).
Type 2 MI: The “Supply vs. Demand” Problem
Mechanism: Ischaemia occurs without acute atherothrombosis. It is a mismatch between how much oxygen the heart needs and how much it gets.
Common Triggers: * Reduced Supply: Severe anaemia, hypotension, hypoxaemia, or coronary artery spasm.
Increased Demand: Severe tachycardia (e.g., AF with RVR), sepsis, or hypertensive crisis.
Management: Treat the underlying cause first (e.g., give a blood transfusion for anaemia, or slow the heart rate in AF). You do not usually give DAPT or offer urgent PCI unless there is evidence of concurrent obstructive CAD.
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – Comparison Table
| Feature | Type 1 MI | Type 2 MI |
| Primary Cause | Plaque rupture + Thrombosis | Supply/Demand imbalance |
| Troponin | Elevated (Dynamic) | Elevated (Dynamic) |
| ECG Changes | Common (ST elevation or depression) | Common (often ST depression/T-wave inversion) |
| Angiography | Shows thrombus/occlusion | Often shows stable CAD or normal arteries |
| Mnemonic | “The ACDC MI” (ACS-type) | “The Can’t Cope MI” (Heart can’t cope with demand) |
Mechanism-Based Management Highlights
🧠 Refer to ACS section for comprehensive protocol, but note:
Antiplatelet therapy (Aspirin + P2Y12 inhibitor) targets arterial thrombosis
Anticoagulation (e.g. fondaparinux) in NSTEMI
Thrombolysis if PCI not available within 120 minutes (STEMI)
PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention) – definitive treatment
Statins + ACE-i/ARB + Beta-blockers post-event
Long-Term Considerations
Lifestyle modification
Cardiac rehabilitation
Antiplatelets and statins long-term
Risk factor optimisation (BP, glucose, lipids)
Last updated in line with:
NICE NG185 (2025/26 Consolidated Update): Replacing separate CG167 (STEMI) and NG185 (NSTEMI) targets with a unified ACS “Invasive-First” framework.
ESC ACS Guidelines (2025 Focused Update): Addressing the shift towards P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy after 1–3 months in high-bleeding-risk patients.
UDMI-5 (2026): The 5th Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction, emphasizing the Type 1 vs. Type 2 distinction.
PARA/MLA-aligned: Fully reviewed February 2026 for current exam blueprints.
🔒 PASSMAP Assurance: This content is peer-reviewed, NICE-compliant, and optimised for the GMC Medical Licensing Assessment (MLA) and PA National Exam (PARA).
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
