2. Gastro-intestinal Ulcer Disease (GUD)
 Definition
Definition
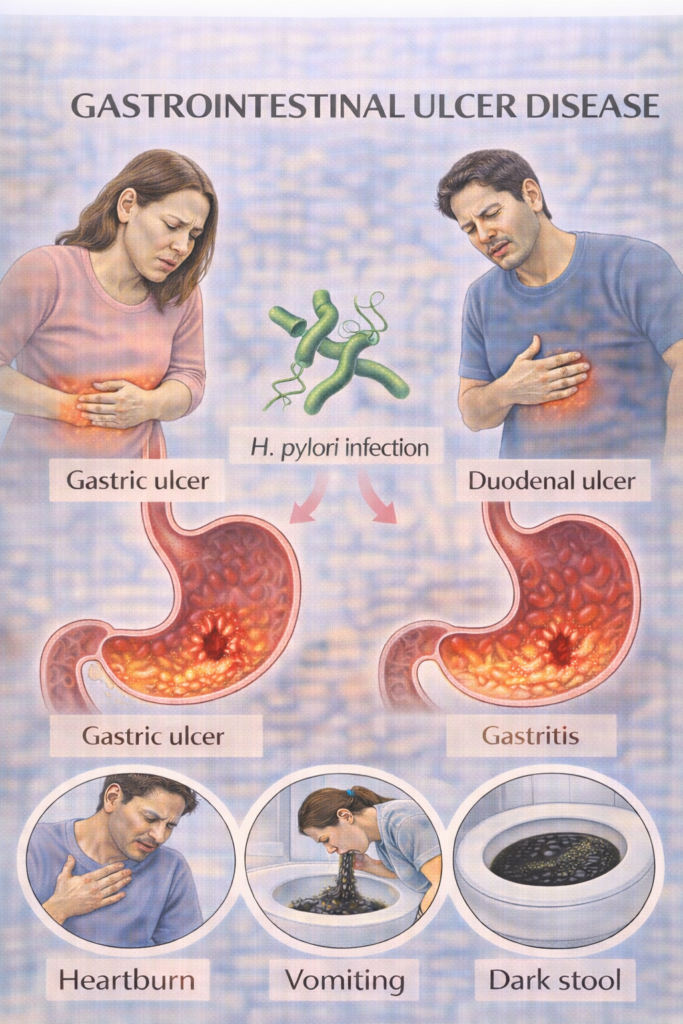
Mucosal ulceration in the stomach (gastric ulcer) or proximal duodenum (duodenal ulcer), due to imbalance between mucosal defences and acid/pepsin exposure.
🛡️ Aetiology / Risk Factors – Mnemonic: SHADE
Smoking
Helicobacter pylori infection
Anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, aspirin)
Duodenal acid hypersecretion
Excess alcohol / emotional stress (less common)
High-risk groups:
Elderly on NSAIDs ± steroids
Previous ulcer/bleed
Chronic anticoagulant use
 Clinical Features (Mnemonic: DUPE)
Clinical Features (Mnemonic: DUPE)
Dyspepsia:
Duodenal ulcer: pain relieved by food, worse at night
Gastric ulcer: pain worsened by food
Ulcer complications: bleeding, perforation, obstruction
Post-prandial fullness / bloating
Epigastric tenderness on palpation
 OGD Referral Criteria:
OGD Referral Criteria:
Refer for urgent endoscopy if:
1️⃣ Urgent – 2 Week Wait (ALARM55)
Anaemia (iron deficiency)
Loss of weight (unintentional)
Anorexia
Recent-onset progressive dysphagia
Melaena / haematemesis
55 – Age ≥55 with new-onset symptoms
2️⃣ Non-Urgent OGD – Without ALARM Features
Age ≥55 with unexplained, persistent dyspepsia
Persistent symptoms after 4–8 week PPI trial + negative H. pylori
Unexplained iron-deficiency anaemia without obvious source
🔬 Investigations
If NO red flags →
Test for H. pylori before OGD in most cases
1st-line: Urea breath test or stool antigen
Stop PPI ≥2 weeks before testing
Consider FBC (anaemia), LFTs/amylase (differentials)
If red flags present →
Urgent OGD
Gastric ulcer → biopsy to exclude malignancy
CLO test or histology for H. pylori
Follow-up OGD
Gastric ulcer – always re-scope at 6–8 weeks to confirm healing
Duodenal ulcer – no routine re-scope if H. pylori eradicated & symptoms resolved
💊 Management (Mnemonic: HOPER)
1️⃣ H. pylori eradication (if positive)
Triple therapy × 7 days:
PPI + clarithromycin + amoxicillin
Metronidazole if penicillin-allergic
Confirm eradication ≥4 weeks post-treatment (off PPI ≥2 weeks)
2️⃣ Omeprazole (PPI) – healing therapy
Omeprazole 20–40 mg OD × 4–8 weeks
3️⃣ Prevention (NSAID users)
Stop NSAIDs if possible
If unavoidable: co-prescribe PPI, eradicate H. pylori first
4️⃣ Endoscopy follow-up
As above – re-scope gastric ulcers, not routine for duodenal ulcers
5️⃣ Risk factor modification
Stop smoking
Limit alcohol/caffeine/spicy foods
⚠️Complications (Mnemonic: BAPH)
Bleeding – may present with haematemesis or melaena
Anaemia – iron deficiency from chronic blood loss
Perforation – presents with acute abdomen
Hourglass deformity – from fibrosis/scarring (rare)
💡Key Exam Traps for PARA MCQs
Gastric ulcer pain worse with food, duodenal relieved by food
Always biopsy gastric ulcers to exclude cancer
Stop PPIs 2 weeks before H. pylori testing — common MCQ distractor
NSAID use + ulcer → stop NSAID, treat H. pylori, give PPI
Only gastric ulcers need repeat OGD
Bleeding risk rises with SSRIs, steroids, anticoagulants
 Differentiating Gastric vs Duodenal Ulcers
Differentiating Gastric vs Duodenal Ulcers
| Feature | Gastric Ulcer | Duodenal Ulcer |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | Worsened by food | Relieved by food |
| Risk of malignancy | Yes (requires biopsy) | Rare |
| Common in | Older adults | Younger patients |
| Location | Lesser curvature of stomach | First part of duodenum |
Last updated in line with NICE CG184 (Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and dyspepsia in adults: investigation and management)
Published: November 2014 • Last updated: October 2019
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
PASSMAP ensures all content is NICE-aligned and reviewed for Physician Associate Registration Assessment (PARA) success.
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
