16. Haemachromatosis
📄 Definition
Hereditary haemochromatosis is an autosomal recessive iron overload disorder (most often HFE gene mutation, esp. C282Y homozygote) → increased intestinal iron absorption → progressive iron deposition in the liver, pancreas, heart, skin, joints, and endocrine organs.
🛡️ Epidemiology & Risk
Common in Northern European ancestry (esp. Celtic).
Rare in South Asians / Afro-Caribbean populations.
Male > female (women protected by menstruation/pregnancy until menopause).
Age of onset: usually 40–60 yrs.
🔬 Pathophysiology
HFE gene mutation → ↓ hepcidin → ↑ ferroportin activity → excessive gut iron absorption.
Iron accumulates in hepatocytes → oxidative stress → fibrosis → cirrhosis/HCC risk.
Deposition elsewhere → pancreas (diabetes), skin (pigmentation), heart (cardiomyopathy), joints (arthropathy).
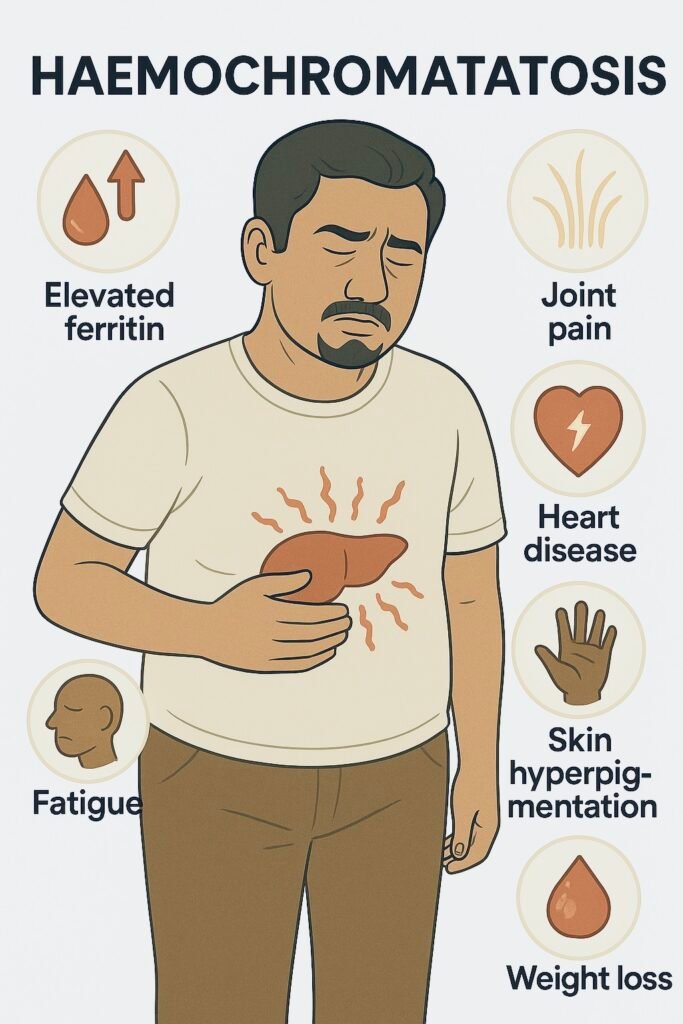
🤒 Clinical Features (Mnemonic: “BRONZE DIABETES”)
Bronze skin pigmentation.
Diabetes mellitus (“bronze diabetes”).
Arthropathy (MCP joints, esp. 2nd/3rd).
Liver: hepatomegaly, cirrhosis, ↑ HCC risk.
Other: fatigue, impotence, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia, hypogonadism.
🔬 Investigations (Stepwise PARA Focus)
| Step | Test | Findings / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Initial | Serum ferritin & transferrin saturation (TSAT) | Ferritin ↑ (>300 men, >200 women); TSAT >45% diagnostic clue. |
| 2️⃣ Confirmatory | HFE gene testing | C282Y homozygote = diagnostic; C282Y/H63D compound heterozygote = variable penetrance. |
| 3️⃣ Staging | Liver elastography (FibroScan) / biopsy | Assess fibrosis/cirrhosis (biopsy if ferritin >1000 or high suspicion of advanced disease). |
| 4️⃣ Other | FBC, LFTs, fasting glucose/HbA1c, ECG/echo | Assess complications (diabetes, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia). |
💡 Ferritin alone is nonspecific (raised in inflammation, alcohol, MASLD). Always check TSAT.
📋 Management (Stepwise – BSG/NICE aligned)
| Step | Treatment | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ First-line | Venesection (phlebotomy) | Weekly/fortnightly until ferritin 20–50 µg/L and TSAT <50%. Lifelong maintenance thereafter (3–4 per year). |
| 2️⃣ Alternatives | Iron chelation (deferasirox, desferrioxamine) | If venesection contraindicated (rare). |
| 3️⃣ Lifestyle | Avoid iron/vitamin C supplements, minimise alcohol, avoid uncooked shellfish (Vibrio vulnificus risk). | |
| 4️⃣ Complications | HCC surveillance if cirrhosis present (US ± AFP every 6 months). Manage diabetes, cardiomyopathy, arthropathy. | |
| 5️⃣ Family screening | First-degree relatives: genetic testing ± ferritin/TSAT. |
⚠️ Complications
Cirrhosis ± HCC.
Diabetes mellitus.
Cardiomyopathy/arrhythmia.
Arthropathy.
Hypogonadism, osteoporosis.
🔎 Key PARA Exam Traps
💡 TSAT > ferritin = best initial clue (ferritin can be raised in many conditions).
💡 C282Y homozygote = classic mutation.
💡 Venesection = cornerstone (NOT chelation first-line).
💡 Always consider in “middle-aged man with diabetes, arthropathy, abnormal LFTs, bronze skin.”
📅 Last updated in line with
BSG Haemochromatosis Guidelines (2017, reaffirmed 2023)
NICE QS152 (Liver disease)
PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
🔒 PASSMAP ensures all content is PARA-aligned, NICE/BSG-compliant, and exam-ready.
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
