13. Pancreatitis
 Definition
Definition
Acute or chronic inflammation of the pancreas due to premature activation of pancreatic enzymes, leading to autodigestion, inflammation, and systemic complications.
 Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology
-
Enzyme activation (trypsinogen → trypsin) → autodigestion.
-
Triggers: gallstones, alcohol, hypertriglyceridaemia, trauma, ERCP, drugs.
-
Can → necrosis, pseudocyst, systemic inflammatory response (SIRS).
 Causes (Mnemonic: I GET SMASHED)
Causes (Mnemonic: I GET SMASHED)
-
Idiopathic
-
Gallstones (most common UK)
-
Ethanol
-
Trauma
-
Steroids
-
Mumps / viral infections
-
Autoimmune
-
Scorpion sting (rare)
-
Hyperlipidaemia / Hypercalcaemia
-
ERCP (Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography)
-
Drugs (azathioprine, valproate, thiazides, tetracyclines)
📋 Clinical Features
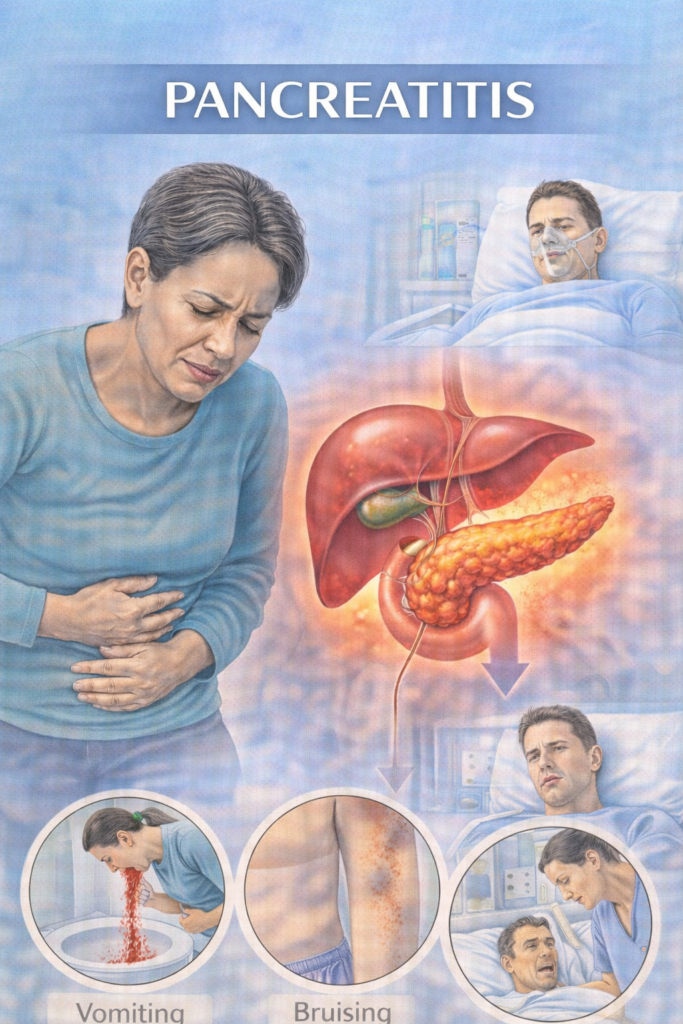
Severe epigastric pain radiating to back, relieved by sitting forward
Nausea, vomiting, anorexia
Abdominal tenderness ± guarding
Fever, tachycardia, hypotension
Severe: Grey-Turner’s sign (flank bruising), Cullen’s sign (periumbilical bruising)
🔬 Investigations (Stepwise PARA Focus)
| Step | Investigation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Initial | Serum amylase or lipase (>3× ULN) | Diagnostic (lipase preferred) |
| FBC, CRP, U&E, LFTs, glucose, calcium, ABG | Assess severity & complications | |
| 2️⃣ Imaging | USS abdomen | Look for gallstones / biliary cause |
| CT abdomen (contrast) | Confirm, stage necrosis, complications (best after 72 hrs) | |
| 3️⃣ Prognostic | Glasgow-Imrie score, CRP >150, APACHE II | Predict severity |
 Glasgow Score (PANCREAS) – Assess within 48 hrs
Glasgow Score (PANCREAS) – Assess within 48 hrs
| Criterion | Cut-off | Score |
|---|---|---|
| PaO₂ | < 8 kPa (60 mmHg) | +1 |
| Age | > 55 years | +1 |
| Neutrophils (WCC) | > 15 × 10⁹/L | +1 |
| Calcium | < 2.0 mmol/L | +1 |
| Renal function (Urea) | > 16 mmol/L | +1 |
| Enzymes (LDH) | > 600 U/L | +1 |
| AST/ALT | > 200 U/L | +1 |
| SugarGlucose) | > 10 mmol/L | +1 |

Score 0–2 → mild pancreatitis
Score ≥3 → severe pancreatitis (↑ risk of complications/mortality)
💊 Management of Acute Pancreatitis (UK – NICE / BSG)
| Step | Intervention | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ Immediate (within first hours) | ABCDE resuscitation + High-flow O₂ | Assess airway, breathing, circulation early |
| IV fluids (0.9% NaCl / Hartmann’s) | Cornerstone – aggressive hydration reduces necrosis risk | |
| Analgesia (opioids e.g. IV morphine / pethidine) | Paracetamol adjunct; opioids usually required | |
| Nil by mouth (NBM) | Pancreatic rest – avoid oral intake initially | |
| 2️⃣ Monitoring | Vital signs + urine output | Strict fluid balance |
| Bloods: FBC, U&E, LFTs, calcium, glucose, CRP | Serial monitoring to guide severity | |
| Glasgow score at 48 hrs | Stratifies severity; guides escalation | |
| 3️⃣ Specific | Treat underlying cause | • Gallstones → ERCP ≤72 hrs if obstruction/cholangitis • Alcohol → withdrawal support |
| 4️⃣ Nutrition | Enteral feeding (NG/NJ) if >48 hrs NBM or severe case | Avoid TPN unless enteral not tolerated |
| 5️⃣ Complications | Infected necrosis | IV antibiotics + drainage |
| Pancreatic abscess / pseudocyst | Drainage if symptomatic | |
| 6️⃣ Follow-up | Lifestyle advice | Alcohol cessation, weight loss to prevent recurrence |
🧠 Exam mnemonic: PANCREAS (just like the Glasgow score, works for management too!)
Pain relief (opioids)
Aggressive IV fluids
NBM (then enteral feeding if prolonged)
Cause treatment (ERCP, alcohol withdrawal)
Review obs + labs
Electrolyte correction
Antibiotics only if infected necrosis (NOT prophylactic)
Severity assessment (Glasgow score)
⚠️ Complications of Acute Pancreatitis
| Timing | Complication | PARA Recall Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Early (systemic) | Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) | Widespread inflammation → tachycardia, fever, tachypnoea |
| Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) | Severe hypoxaemia, non-cardiogenic pulmonary oedema | |
| Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) | Oliguria, ↑creatinine from hypoperfusion | |
| Shock | Hypovolaemic/septic → needs aggressive fluids | |
| Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) | Bleeding + clotting abnormalities (↑PT, ↓platelets) | |
| Late (local) | Pancreatic Pseudocyst | Fluid collection >4 weeks, may rupture/infect |
| Pancreatic Abscess | Infected necrosis → sepsis risk | |
| Pancreatic Necrosis | Sterile or infected; needs drainage if infected | |
| Chronic Pancreatitis | Long-term pain, exocrine/endocrine insufficiency | |
| Diabetes Mellitus | Due to endocrine destruction (islet cell loss) | |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Increased risk after chronic inflammation |
🔎 Key PARA Exam Traps
Lipase > amylase (more specific & sensitive).
CRP >150 at 48h = severe pancreatitis.
Antibiotics NOT for sterile necrosis.
Cullen’s / Grey-Turner’s = haemorrhagic pancreatitis.
Always check calcium & triglycerides in “non-gallstone, non-alcohol” cases.
- PARA-aligned, reviewed February 2026
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
