4. Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
 Definition
Definition
Cystic Fibrosis is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, leading to defective chloride transport and production of thick, sticky secretions affecting the lungs, pancreas, gastrointestinal tract, and reproductive system.
 EXAM ANCHOR – CORE CONCEPT (PARA)
EXAM ANCHOR – CORE CONCEPT (PARA)
- CF = autosomal recessive CFTR mutation
- Defective chloride transport → thick, sticky secretions
- Multisystem disease (lungs, pancreas, GI, reproductive)

Which genetic disorder causes thick, sticky secretions due to CFTR dysfunction?
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – INHERITANCE
Autosomal recessive inheritance
Both parents must be carriers
Siblings at increased risk

What is the mode of inheritance of cystic fibrosis?
 Physical Examination Findings
Physical Examination Findings
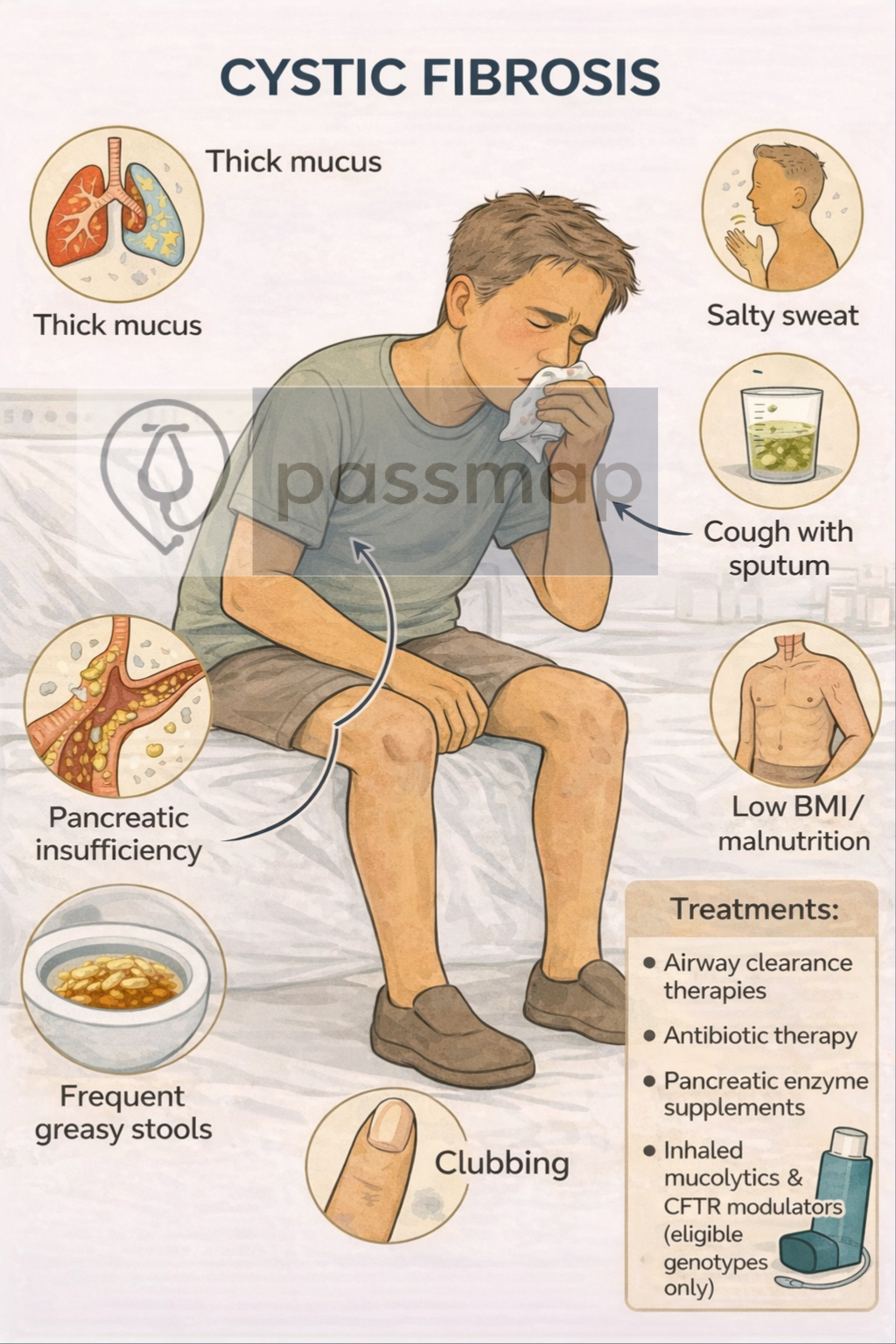
- Chronic productive cough
- Coarse crackles ± wheeze
- Finger clubbing
Signs of advanced disease:
Pulmonary hypertension
Cor pulmonale
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – RESPIRATORY MANIFESTATIONS
Chronic productive cough
Recurrent chest infections
Bronchiectasis develops over time (irreversible)
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which chronic lung complication commonly develops in cystic fibrosis?
🔎 Investigations
🧠 Mnemonic: SWEEP BUGS
S — Screening (Most Common Initial)
Newborn blood spot (Guthrie/heel-prick) test measuring immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT).
Confirmatory (gold standard): Sweat chloride test — a result >60 mmol/L confirms cystic fibrosis.
Genetic testing: Used when the sweat chloride result is intermediate (30–59 mmol/L) or to identify specific CFTR mutations (e.g. F508del) for CFTR modulator eligibility.
W — Whole CFTR genetic testing
Confirms mutation
Determines CFTR modulator eligibility
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – DIAGNOSIS
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What is the gold standard diagnostic test for cystic fibrosis?
E — Exocrine pancreatic function
Faecal elastase ↓
Explains steatorrhoea & malnutrition
E — Exercise oxygen saturation
Desaturation in advanced disease
P — Pulmonary function tests
Obstructive pattern
Progressive ↓ FEV₁ over time
B — Bronchiectasis on High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT)
Dilated airways
Mucus plugging
Tree-in-bud opacities
 EXAM ANCHOR – IMAGING (PARA)
EXAM ANCHOR – IMAGING (PARA)
Sweat chloride test = diagnostic gold standard
Elevated sweat chloride confirms CF
Genetic testing supports diagnosis

What is the typical HRCT chest finding in cystic fibrosis?
Answer: Bronchiectasis with mucus plugging
U — Upper GI / neonatal history
Meconium ileus in neonates (highly suggestive of CF)
G — Glucose testing
Screen for CF-related diabetes
S — Sputum cultures
Identify colonising organisms
Pseudomonas aeruginosa most common
 EXAM ANCHOR – MICROBIOLOGY
EXAM ANCHOR – MICROBIOLOGY

- Commonest organism in children: Staphylococcus aureus (often managed with prophylactic Flucloxacillin). Commonest in adults: Pseudomonas aeruginosa.”
Which organism in adults is most commonly colonises the lungs in cystic fibrosis?
Answer: Pseudomonas aeruginosa
 Management
Management

Chest physiotherapy
Daily airway clearance is essential
Cornerstone of long-term management
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLE
Daily airway clearance is essential
Long-term multidisciplinary specialist care required
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What is the cornerstone of long-term respiratory management in cystic fibrosis?
Other Key Management Components
Long-term antibiotics (e.g. azithromycin)
Pancreatic enzyme replacement (Creon)
High-calorie, high-protein diet
Nebulised bronchodilators + mucolytics (e.g. DNase)
Antibiotics for exacerbations (oral/IV guided by culture)
Annual screening for CF-Related Diabetes (CFRD) from age 10 using an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT).
Note: HbA1c is not recommended for diagnosis in CF)
Oxygen / NIV if progressive disease
Vaccinations (annual flu, pneumococcal)
Smoking avoidance
Specialist multidisciplinary CF team care
 EXAM ANCHOR – PANCREATIC INVOLVEMENT
EXAM ANCHOR – PANCREATIC INVOLVEMENT
Pancreatic insufficiency is common
Causes steatorrhoea & weight loss
Requires enzyme replacement

What causes steatorrhoea and weight loss in cystic fibrosis?
CFTR Modulators (e.g. ivacaftor, lumacaftor–ivacaftor) for eligible genotypes
Lung transplant in end-stage disease
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – TARGETED THERAPY
CFTR modulators (e.g. ivacaftor, lumacaftor–ivacaftor)
Target the underlying CFTR defect
Only effective in eligible genotypes
📌 PARA commonly asks:
Which therapy targets the underlying CFTR defect in cystic fibrosis?
⚠️ Complications
Bronchiectasis
Respiratory failure
Infertility (especially males)
CF-related diabetes
Osteoporosis
Liver disease
Intestinal obstruction
Pneumothorax
Haemoptysis
Psychological impact
🎯 EXAM ANCHOR – FERTILITY
Male infertility is common
Due to congenital absence of the vas deferens
📌 PARA commonly asks:
What reproductive complication commonly affects males with cystic fibrosis?
🧐Differentials
🧠 Mnemonic: SAME FAIL
Severe asthma
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA)
Meckel’s diverticulum (if bowel obstruction)
Enteropathy
Foreign body inhalation
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
Immunodeficiency
Lung malformations
📌 PARA Revision Tips
Gold standard test = sweat chloride
Most common bug = Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Know Creon, airway clearance, and CFTR modulator therapy
Meconium ileus in newborns = suspect CF
Discuss genetic inheritance and screening
 Key PARA Exam Traps – Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
Key PARA Exam Traps – Cystic Fibrosis (CF)











| Factor | PARA / NICE Standard |
| Sweat Test | Chloride > 60 mmol/L |
| Diabetes Screen | OGTT (not HbA1c) annually from age 10 |
| Inheritance | Autosomal Recessive (25% chance if both parents are carriers) |
| Microbiology | S. aureus (Child) → P. aeruginosa (Adult) |
| The “Social” Rule | Patients with CF must never meet in person (risk of cross-infection with Burkholderia cepacia). |

Last reviewed: February 2026
Educational platform. Not medical advice.
